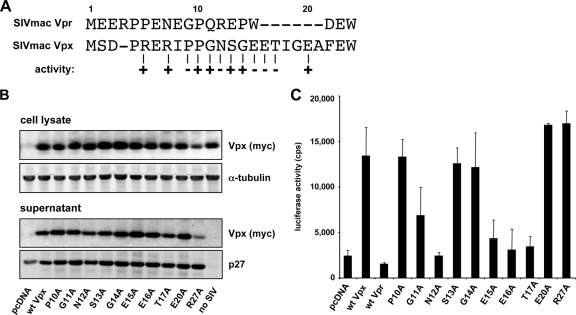
FIG. 5.
Analysis of the Vpx amino terminus. (A) An alignment of the SIVmac Vpx and Vpr amino terminus is shown. Numbers refer to the amino acid position in Vpx. The ability of each Vpx mutant to enhance infection of MDM is indicated as (+) or (−). The arginines at position 5 and 7 and the proline at position 9 were mutated to the corresponding Vpr amino acid (data not shown). Amino acids 10 to 17, 20, and 27 were changed to alanine. (B) Expression and packaging of the amino-terminal mutants. 293T cells were cotransfected with the proviral plasmid pSIVmac Δvpx and an expression plasmid for Vpx, mutated Vpx, or empty vector (pcDNA). Cell lysate and supernatant were analyzed on an immunoblot probed with anti-p27 MAb and anti-myc MAb. No SIV, transfection of Vpx plasmid without the proviral plasmid. (C) Effect of the amino-terminal mutants on SIV infection of MDM. Δvpx SIVmac reporter viruses were complemented with Vpx mutant or empty vector (pcDNA). MDM were infected with the complemented reporter viruses, and luciferase activity was measured after 4 days. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments using MDM prepared from PBMC of three different donors.