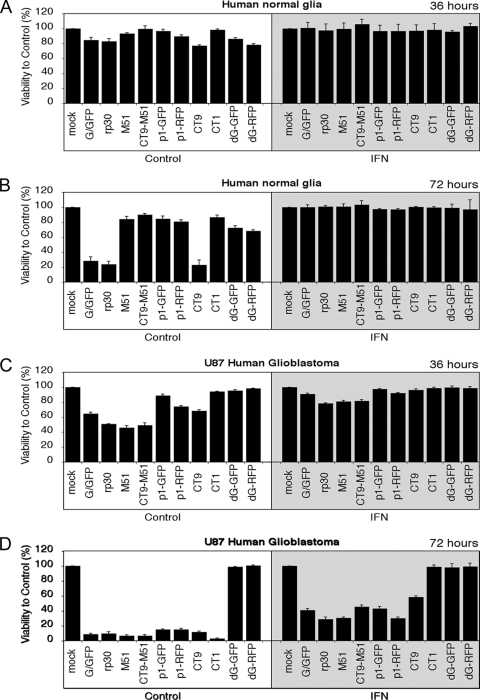
FIG. 3.
Cell viability of human glioblastoma and normal human glia cells after infection with VSV variants. Using an MTT cell viability assay, the cytotoxic effects of 10 VSV variants were tested on human glia control cells and U87 glioblastoma cells. (A) At 36 hpi at an MOI of 0.5, little effect on cell viability was seen for all VSV variants on control cells. (B) VSV-G/GFP, VSV-rp30, and VSV-CT9 showed signs of toxicity after 72 h. The presence of IFN (shaded boxes) completely protected normal human glia cells from infection with all VSV variants. (C) Human U87 glioblastoma cells showed a pronounced loss of viability at 36 hpi with 6 of 10 VSV variants. (D) At 72 hpi, all VSV variants, except the two replication-restricted VSV-dG mutants, completely killed U87 cells. Interferon provided little protection for U87 cells at 72 hpi (shaded box).