FIG. 5.
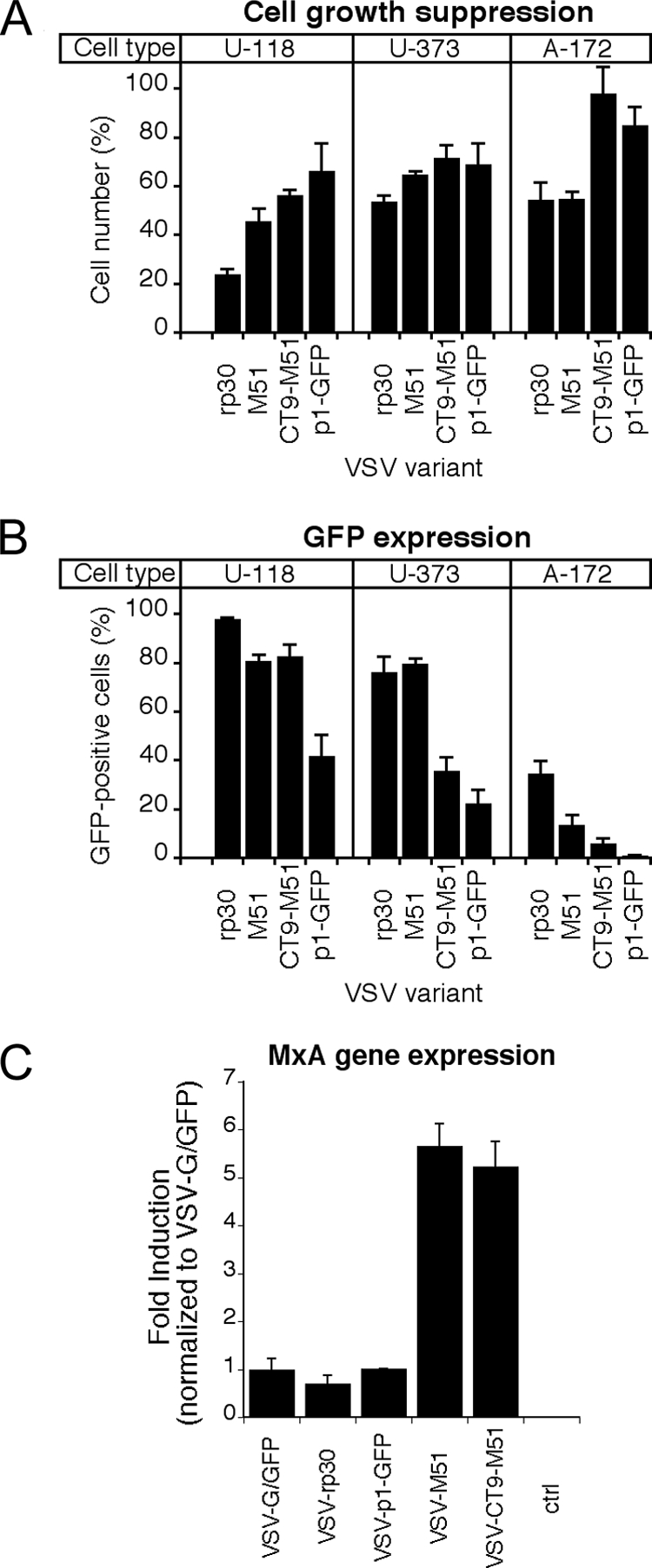
Infection and growth suppression of alternate human glioma cultures and MxA gene induction of VSV variants on control cells. Tumor cell infectivity and growth suppression were tested for human glioblastoma cell types U118, U373, and A-172. VSV variants VSV-rp30, VSV-M51, VSV-CT9-M51, and VSV-p1-GFP were applied at an MOI of 2 and analyzed at 24 hpi. (A) As on U87 cells, VSV-rp30 had the strongest growth-suppressing effect, and VSV-CT9-M51 and VSV-p1-GFP suppressed tumor growth to a lesser extent. (B) GFP fluorescence revealed a similar picture, with VSV-rp30 having the highest rates of infection compared to the attenuated VSV variants. Bars show mean values for five microscopic fields. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means. (C) Using quantitative real-time PCR, the expression of the interferon-induced antiviral gene MxA was compared after infection of cells with VSV-G/GFP, VSV-rp30, VSV-p1-GFP, VSV-M51, and VSV-CT9-M51. M51 mutation-containing mutants induced about 5 to 6 times more MxA than did VSV variants with wild-type M protein. Results are means for triplicate cultures. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means.
