FIG. 6.
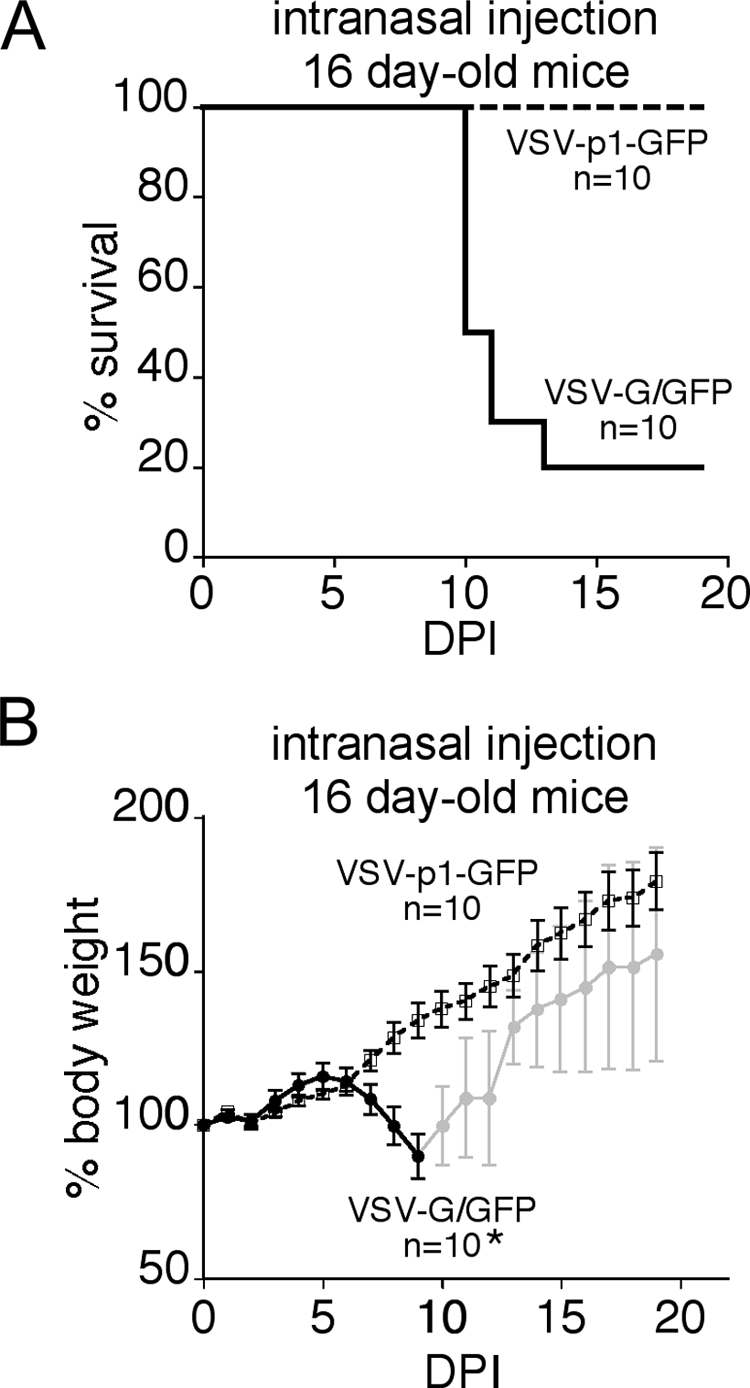
Intranasal application of VSV-G/GFP and VSV-p1-GFP. VSV has been shown to cause neurotoxicity in young mice when administered through an olfactory entry route. A total of 500,000 PFU of either wild-type-related VSV-G/GFP or attenuated VSV-p1-GFP was inoculated intranasally into young mice. The mice lost body weight after VSV-G/GFP inoculation (B), and 8 of 10 mice ultimately succumbed (A). In contrast, littermates that received VSV-p1-GFP gained weight steadily, and no mortality was seen. n = 10, the number of mice initially infected with the virus.
