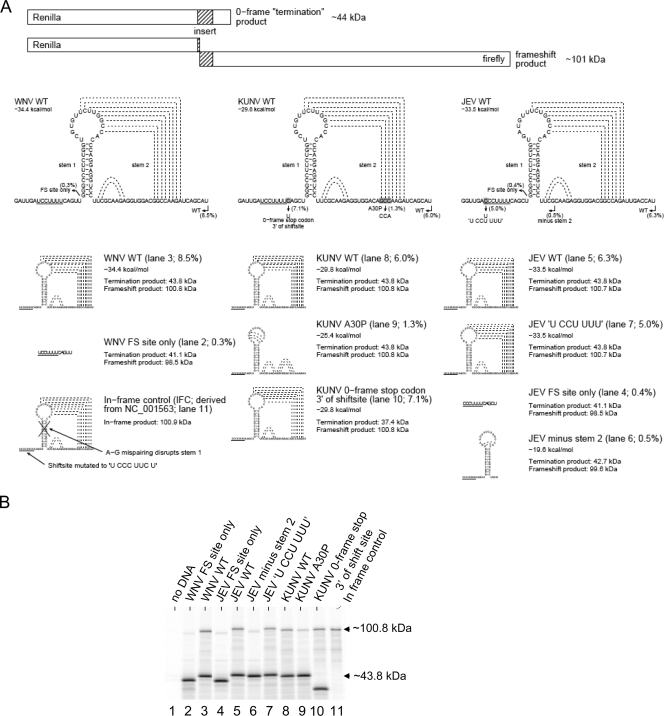
FIG. 3.
Sequence requirements for −1 ribosomal frameshift in vitro. (A) Diagram of the dual-luciferase reporter system and predicted structures of the WT and mutant sequences used to evaluate the role of WNV, KUNV, and JEV viral sequences in −1 ribosomal frameshifting. Production of an ∼101-kDa product is observed if the inserted sequence induces frameshifting. Locations of different stimulatory elements and mutations are shown as underlined or highlighted sequences. Putative interactions between bases are shown as dashed lines. Frameshifting efficiencies calculated from the intensity of labeled bands in panel B, after normalization for the number of methionine residues in each product, are shown next to the lane numbers in parentheses. (B) SDS-PAGE of in vitro translation products of indicated constructs performed in reticulocyte lysates. The molecular masses of Renilla luciferase (no frameshift, ∼44 kDa) and the frameshift product (∼101 kDa; fusion of Renilla and firefly luciferases) are indicated.