FIG. 3.
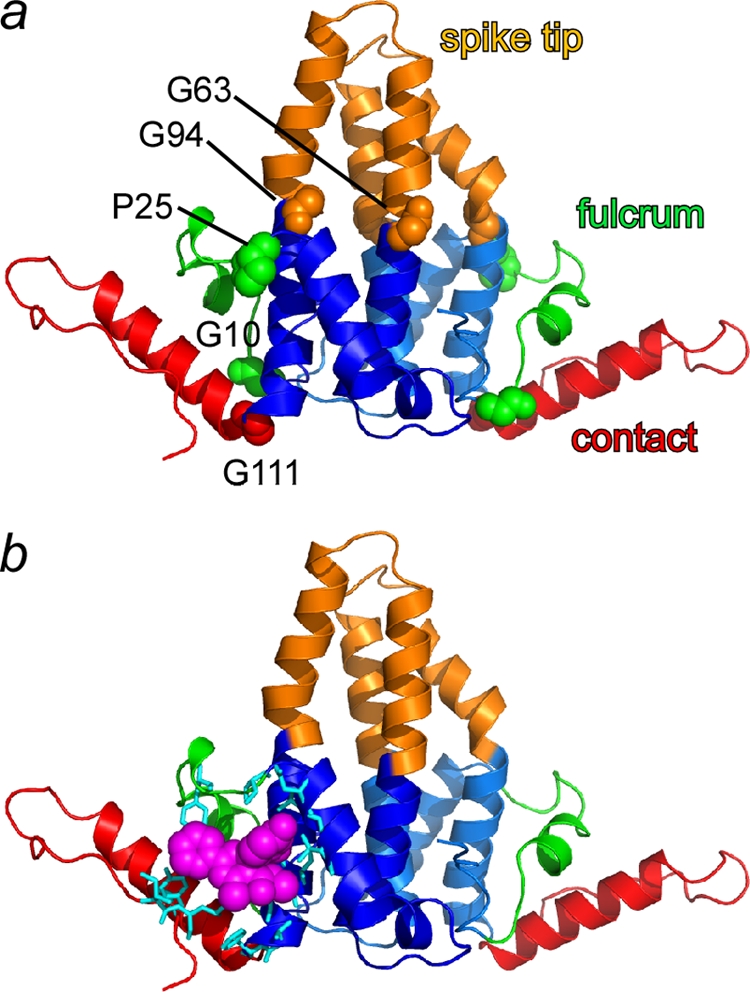
Free dimers have subdomains connected to a chassis by flexible hinges. (a) Based on molecular displacement data (Fig. 2c), subdomains have been color coded and labeled. Domain junctions are flexible hinges (shown in a space-filling representation): Gly10 and Pro25 delineate the fulcrum domain (green), Gly63 and Gly94 delineate the spike tip (copper), and Gly111 is the C-terminal interdimer contact domain (red). The structurally invariant chassis is shown in blue. (b) An assembly effector HAP molecule (magenta) and adjacent residues (cyan), modeled on the basis of a capsid-HAP cocrystal structure (5), noncovalently links the flexible contact and fulcrum domains with the chassis. This stabilization may explain HAP's assembly-accelerating activity.
