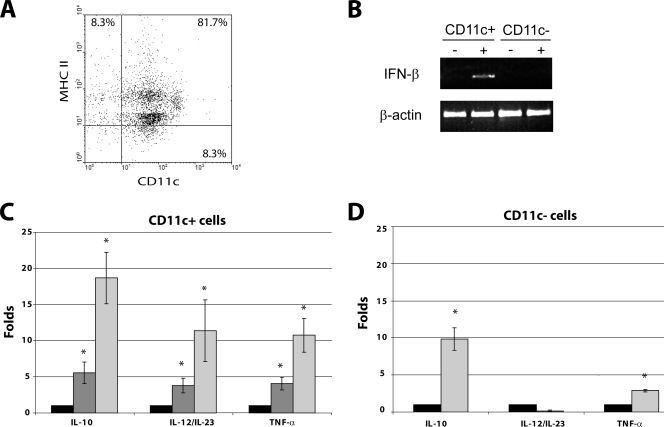
FIG. 4.
RV infection induces the transcription of mRNA for different cytokines in DCs from PPs. Groups of five mice were inoculated orally with 104 FFU of the murine RV EDIMwt, and the PPs from jejunum were obtained at 0, 24, and 48 h p.i. Total cells from PPs were DC enriched by centrifugation using OptiPrep medium, and CD11c+ cells were positively selected using MACS. (A) Dot plot of purified cells from noninfected mice were stained with anti-CD11c and MHC-II MAbs and analyzed by flow cytometry. The data shown are representative of three different experiments. Similar results were obtained with cells from RV-infected mice. (B) mRNA from CD11c+ and CD11c− cells from RV-infected mice at 48 h p.i. was amplified for the IFN-β gene by conventional PCR using specific primers. β-Actin mRNA was used as a constitutive message. +, sample from RV-infected mice; −, sample from noninfected mice. Fold increases for IL-10, IL-12/23p40, and TNF-α mRNA in purified CD11c+ (C) and CD11c− (D) cells of RV-infected mice compared to levels for noninfected mice, as measured by real-time PCR. mRNA for ribosomal 18S proteins was used to normalize the level of the different mRNA. Noninfected mice (black bars) and RV-infected mice at 24 h p.i (gray bars) and 48 h p.i (light gray bars) are shown. Bars represent the standard errors. An asterisk indicates significant difference with respect to control (P < 0.05, Student's t test).