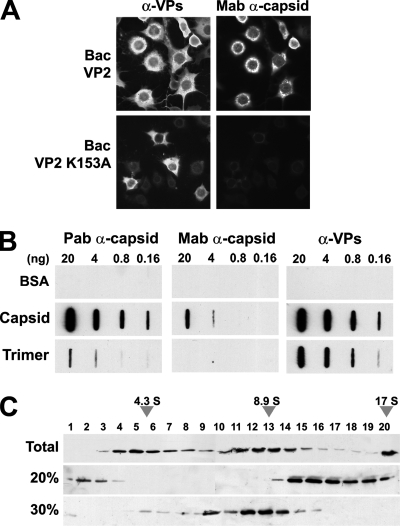
FIG. 1.
MVM capsid trimers accumulate in the cytoplasm of insect cells. (A) Subcellular distribution of MVM structural (VP2) protein (wt and K153A mutant) and capsid in H5 insect cells infected with the indicated recombinant baculoviruses. (B) Antibody specificity for MVM antigens. Capsid and VP trimers gradient-purified from human cells (see Materials and Methods) were applied to nitrocellulose membranes in phosphate saline buffer (PBS), and their immunoreactivity was analyzed by slot blot analyses. Note the lack of reactivity of VP trimers with the monoclonal α-capsid antibody, a finding in agreement with the inability of the trimers to conform in cells the capsid-specific epitope (23, 61). Capsid and VP trimers are efficiently recognized by the α-VPs polyclonal antibody. (C) Purification of VP trimers from insect cells. Extracts of Bac-VP2-K153A-infected H5 cells subjected to ammonium sulfate precipitations were sedimented in sucrose gradients and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Representative results of VP2 distribution in sucrose gradients (including monomers, trimers, and high-molecular-weight aggregates) loaded with total H5 cellular homogenate (upper) or 20% ammonium sulfate precipitate (middle) or in the supernatant of 30% ammonium sulfate precipitation (lower) are shown. The 17 S marker sedimented to the bottom of the gradients.