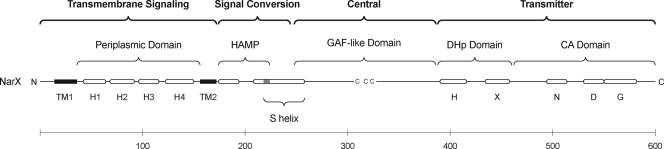
FIG. 1.
NarX modular structure. Linear representation of the NarX protein sequence, from the amino (N) to carboxyl (C) termini, drawn to scale. The four modules are indicated at the top of the figure and shown in bold typeface, whereas domains within each module are labeled with standard (lightface) typeface. The nomenclature for modules follows that devised by Swain and Falke (67) for MCPs. Overlap between the HAMP domain HD2 and S-helix elements is indicated in gray. The three conserved Cys residues within the central module (62) are indicated. TM1 and TM2 denote the two transmembrane helices. Helices H1 to H4 of the periplasmic domain (24), and the transmitter domain H, N, D, G (79), and X (41) boxes, are labeled. The HPK 7 family of transmitter sequences, including NarX, have no F box and an unconventional G box (79). The scale bar at the bottom of the figure shows the number of aminoacyl residues.