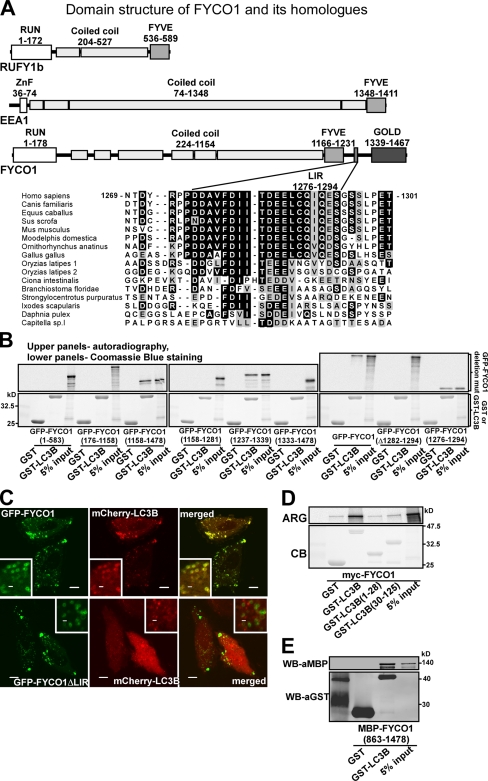
Figure 2.
The interaction between FYCO1 and LC3B is mediated by a short conserved acidic motif C-terminally from the FYVE domain in FYCO1 and both N- and C-terminal domains of LC3B. (A) Schematic structure of FYCO1 and its homologous proteins RUFY1b and EEA1. In the multialignment sequence, identity is indicated by black highlighting, and residues highlighted in gray indicate substitutions to chemically similar amino acids in more than 50% of the compared sequences. (B) The region of FYCO1 between aa 1,276 and 1,294 is essential and sufficient for the interaction with LC3B. GST or GST-LC3B were incubated with [S35]methionine-labeled deletion mutants of FYCO1 and processed as in Fig. 1 C. (C) LIR is essential for colocalization of FYCO1 with LC3B in HeLa cells. HeLa cells expressing the indicated constructs were imaged by confocal microscopy. Insets show an enlarged field of interest. (D) Both N- and C-terminal domains of LC3B are needed for efficient interaction with FYCO1. GST, GST-LC3B, or its deletion mutants were incubated with [S35]methionine-labeled myc-FYCO1 and processed as in Fig. 1 C. ARG, autoradiography; CB, Coomassie blue. (E) The interaction between FYCO1 and LC3B is direct. GST or GST-LC3B was incubated with recombinant MBP-FYCO1863–1,478. Protein complexes were isolated and visualized by immunoblotting with anti-GST or anti-MBP antibodies. WB, Western blot. Bars: (C) 10 µm; (C, insets) 1 µm.