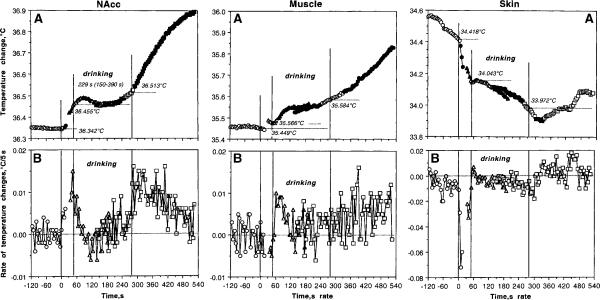
Fig. 3.
Phasic changes in brain (left panel), muscle (central panel), and skin (right panel) temperatures associated with motivated drinking behavior. Top graphs (A) show absolute temperatures and bottom graphs (B) show rate of temperature changes. Three vertical lines in each graph mark the moments of full cup presentation, initiation of drinking behavior, and its end. Horizontal hatched lines in A show mean values of temperatures at the moment of each behavioral event. The hatched line in B shows zero change in temperature, i.e., no difference between each consecutive temperature value. Statistical evaluation was done separately for each of three events, with plus (following) and minus (preceding) time comparisons. Filled symbols show values statistically significant from reference points (either a 5-s value immediately preceding the start and end of drinking or the first 5-s value after these events). F values for cup presentation are: NAcc F32,164=4.88; p<0.001; Muscle=0.58, NS; Skin=52.42, p<0.001. F values for initiation of drinking: (1) preceding drinking onset: NAcc F32,164=36.46, p<0.001; Muscle=1.73, NS; Skin=16.18, p<0.001; (2) following drinking onset: NAcc F32,989=2.36; Muscle=15.05, Skin=4.28, each p<0.001. F values for changes following the end of drinking: (1) preceding end of drinking: NAcc F32,956=5.01; Muscle =6.34, Skin=9.44 (each p<0.001), p=0.59; skin-muscle differential =15.31 (p<0.001); (2) following drinking offset: NAcc F32,1022=57.13 (p<0.001), Muscle =20.17, Skin =2.93 (each p<0.001). While most changes are significant, note quantitative differences in F values that show the strength of the effect.