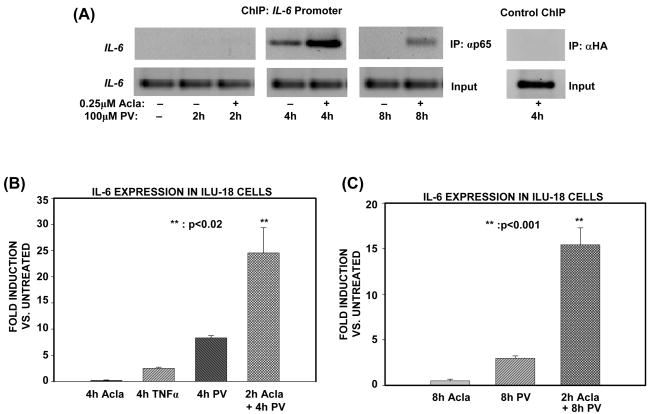
Figure 4. Proteasome limits association of p65/RelA with the IL-6 promoter to terminate atypical, NF-κB-dependent transcriptional responses.
(A). ILU-18 cells were either untreated or treated with PV (100μM) for 2, 4, and 8 hours, with (+) or without (−) pretreatment with Acla (0.25μM) for 2 hours. ChIP assay employing anti-p65 was performed using immunoprecipitated DNA amplified with primers specific for the IL-6 promoter region. ChIP assay employing α-HA (irrelevant antibody) in cells treated with Acla+PV served as a specificity control. Input samples are representative data generated from sonicated DNA fragments not subjected to immunoprecipitation and analyzed by PCR amplification with IL-6 promoter primers.
(B), (C). Equal amounts of RNA were analyzed by real-time PCR detection, after isolation of total RNA from ILU-18 cells treated with TNFα (20ng/mL) or Acla (0.25μM) for 4 hours, or PV (100μM) for 4 hours with or without pretreatment with Acla for 2 hours (B). Data obtained following 8h treatment regimen with PV (100μM), with or without pretreatment with Acla (0.25μM) for 2 hours is presented as fold induction in (C). Fold induction represents treatment-induced IL-6 expression relative to basal IL-6 expression by untreated cells; data represents results from two independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are denoted by **.