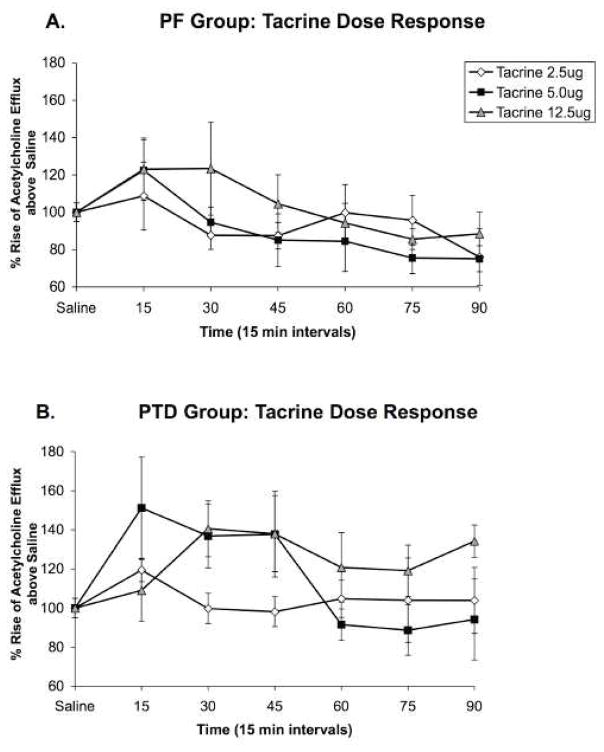
Figure 3. Experiment 2: Hippocampal acetylcholine release after intraseptal saline or tacrine administration.
Profiles of hippocampal acetylcholine release (Mean percent rise above saline ± SEM) after intraseptal tacrine infusions in PF (n = 6; Panel A) and PTD (n = 6; Panel B) animals shown in 15-minute sample bins for 90 min after infusion. The lowest dose of tacrine (2.5 ug) did not alter hippocampal acetylcholine effux in PF or PTD rats. Although the medium (5.0 ug) and high (12.5 ug) doses of tacrine infused into the medial septum increased hippocampal acetylcholine efflux in both PF and PTD rats, the percent change in acetylcholine efflux was greater in PTD rats (all P’s < 0.05).