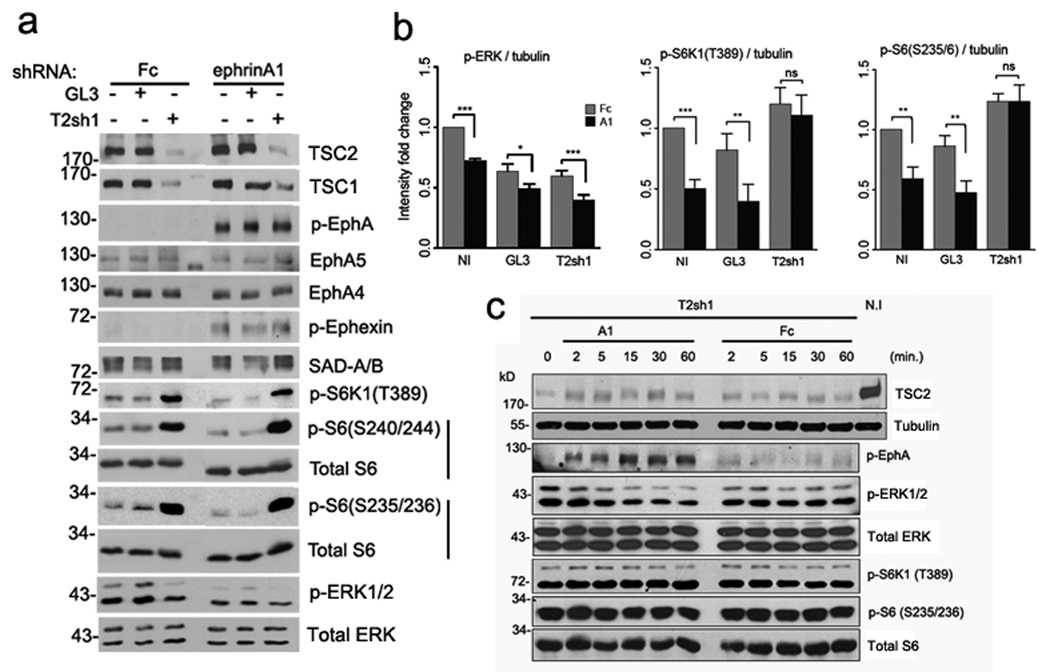
Figure 7. Tsc2 is required for the ephrin-A1-stimulated mTOR inactivation.
Tsc2+/+ cortical neurons were infected with lentivirus expressing shRNA against Tsc2 (T2sh1) or a firefly luciferase (GL3, control). Non-infected (N.I.) as well as the infected neurons were then stimulated with pre-clustered ephrin-A1-Fc versus Fc for 30 minutes. (a) Representative western blots for indicated proteins. Downregulation of Tsc2 decreased Tsc1 levels and increased SAD-A/B levels, consistent with our previous studies17, 24. There were no significant differences in EphA4 and EphA5 expression, ephrin-induced EphA tyrosine phosphorylation or in ephexin phosphorylation between Tsc2 knockdown and control neurons. Tsc2 knockdown abolished the ephrin-A1-dependent downregulation of S6K1 and S6 phosphorylation observed in control neurons. Inactivation of ERK1/2 by ephrin-A1 was still observed in the Tsc2 knockdown neurons, even though the baseline level of phospho-ERK1/2 was lower in these neurons than in the controls. Total ERK1/2, S6 are used as loading controls. Full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Figure S14. (b) Quantification of the western blot analyses. Relative intensities for each protein were normalized according to the tubulin loading control and expressed as mean ratios of GL3 or T2sh1 to non-infected (NI) neurons in each independent experiment. Data represent mean ± SEM from 4 independent experiments (*P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 and ns=not significant). (c) T2sh1-infected neurons were stimulated with pre-clustered ephrin-A1-Fc or control Fc proteins for the time periods as indicated. Phospho-S6K1 and phospho-S6 remained unchanged over the time course of stimulation. Tubulin, total ERK, S6K and S6 were used as loading controls.