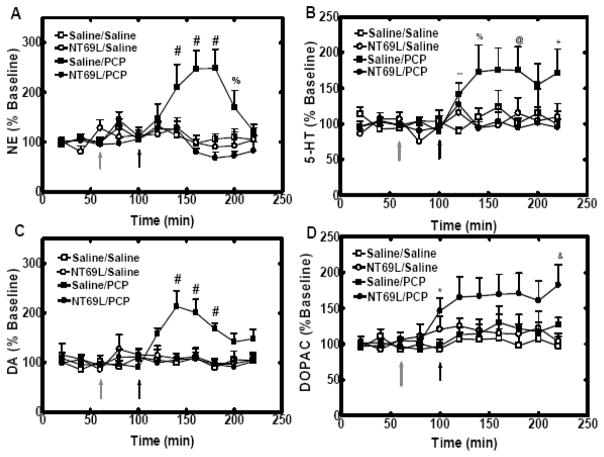
Figure 3.
In panels A, NT69L blocked the PCP-induced increase of NE levels in mPFC. In panels B, NT69L blocked the PCP-induced increase of 5-HT levels in mPFC. In panels C, NT69L blocked PCP-induced increases of DA levels in mPFC. In panels D, NT69L increased DOPAC levels in mPFC. All data are shown as the % baseline of monoamines measured every 20 min (±S.E.M.). (N=5 for Saline/PCP group, Saline/Saline group and NT69L/Saline group, N=6 for NT69L/PCP group). %, P<0.05 versus NT69L/Saline and NT69L/PCP groups. *, P<0.05 NT69L treated groups versus Saline treated groups. &, P<0.05 versus NT69L/Saline and Saline/Saline groups. #, P<0.05 versus Saline/Saline, NT69L/Saline and NT69L/PCP groups. @, P<0.05 versus Saline/Saline and NT69L/PCP groups. **, P<0.05 versus Saline/Saline group. +, P<0.05 versus NT69L/PCP group. Gray arrow indicates when rats received either saline or NT69L injection. Black arrow indicates when rats received either saline or PCP injection.