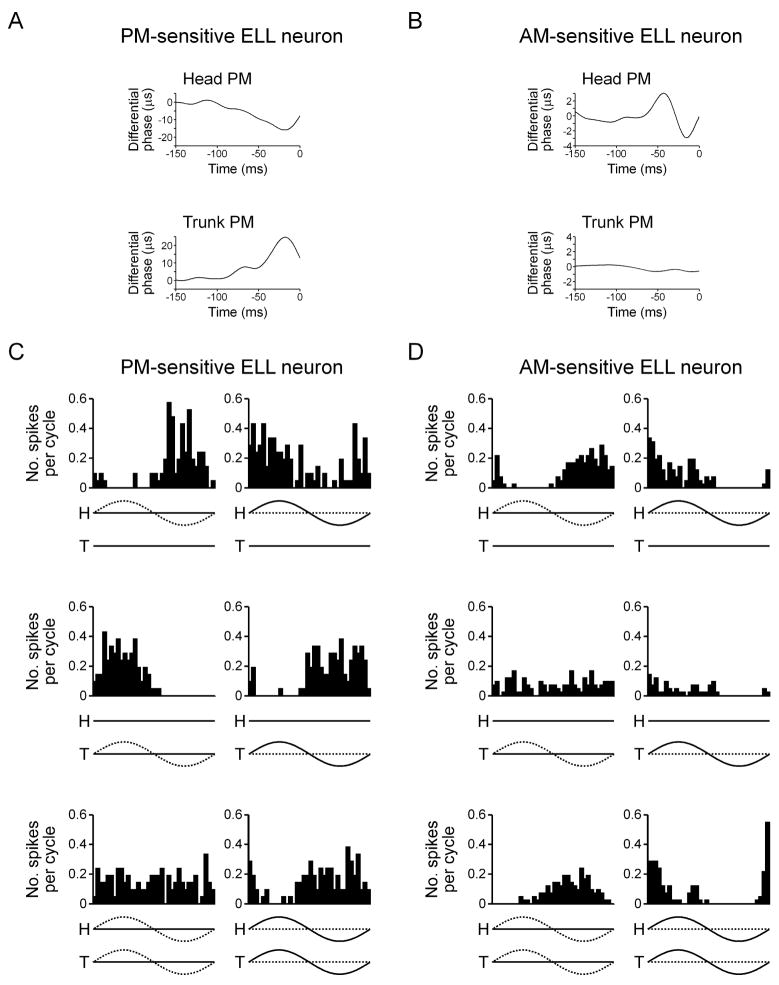
Fig. 6.
PM-sensitive ELL neurons are responsive to differential modulation, whereas AM-sensitive ELL neurons typically are not. (A,B) Spike-triggered average phase from a PM-sensitive ELL neuron (A) and AM-sensitive ELL neuron (B) during random PM presented to the head compartment (trunk unmodulated) and trunk compartment (head unmodulated). (C,D) Histograms of spike times relative to the modulation cycle for a PM-sensitive ELL neuron (C) and AM-sensitive ELL neuron (D) during sinusoidal PM (left column) and sinusoidal AM (right column) presented to the head compartment (top row), trunk compartment (middle row), and both compartments (bottom row). Below each histogram, the amplitude of the signal is represented by a solid line and the phase of the signal is represented by a dashed line, with ‘H’ referring to the head compartment, and ‘T’ referring to the trunk compartment.