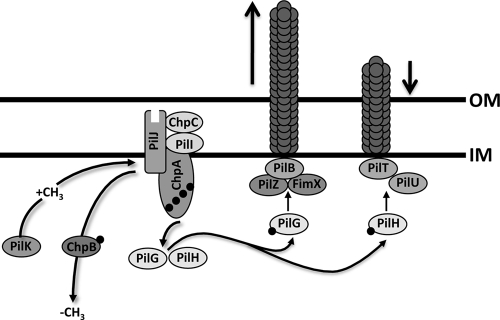
FIG. 1.
Model for the regulation of type IV pilus function by the Chp chemosensory system. The hybrid histidine kinase ChpA, likely associated with the inner membrane, is coupled to a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein receptor, PilJ, by one of two CheW adaptor protein homologues, PilI and ChpC. Upon receipt of a yet-to-be-elucidated signal, PilJ undergoes a conformational change causing ChpA to autophosphorylate. Phosphate groups are transferred from ChpA to two CheY-like response regulator proteins, PilG and PilH. PilG-P interacts with a motor complex including PilZ, the diguanylate cyclase FimX, and ATPase PilB to mediate pilus extension. PilH-P interacts with ATPases PilT and/or PilU to mediate pilus retraction. Adaptation to the chemical signal is mediated through methylation of PilJ by the competing activities of the methyltransferase PilK and the methylesterase PilB.