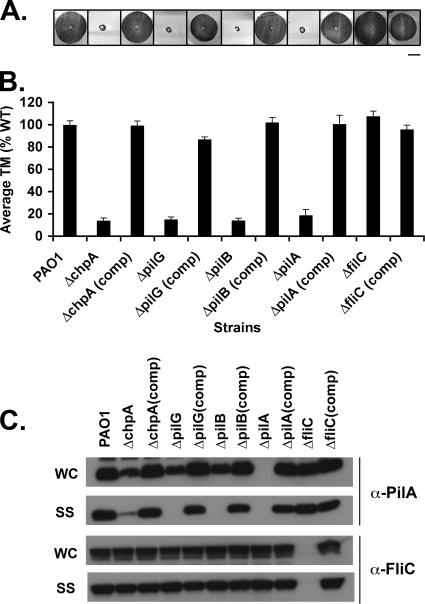
FIG. 2.
Assays of pilus function for mutants defective in pilus extension. (A) Subsurface TM assay of PAO1, the indicated in-frame deletion mutants, and complemented (comp) strains in which the wild-type gene was reintroduced at its endogenous locus. TM assays were performed by the subsurface stab method, followed by Coomassie blue staining, as described previously (1). Bar, 1 cm. (B) Graph depicting TM zone diameters for the indicated strains. The diameter is expressed as a percentage of PAO1 TM. Shown are the means ± the standard deviation (SD, n = 5). The residual zones observed in ΔpilA, ΔchpA, ΔpilG, and ΔpilB strains represent colony growth. (C) Intracellular and surface pilin and flagellin levels. For the indicated strains, surface structures (SS) including pili and flagella were sheared by vigorous vortexing of bacteria cultured on solid media and separated from cells (WC) by centrifugation. The sheared pili and flagella were precipitated. WC (15 μg of total protein) and SS (5% of the total resuspended volume of the precipitate) samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with a polyclonal antibody to PilA (α-pilA) or to FliC (α-FliC).