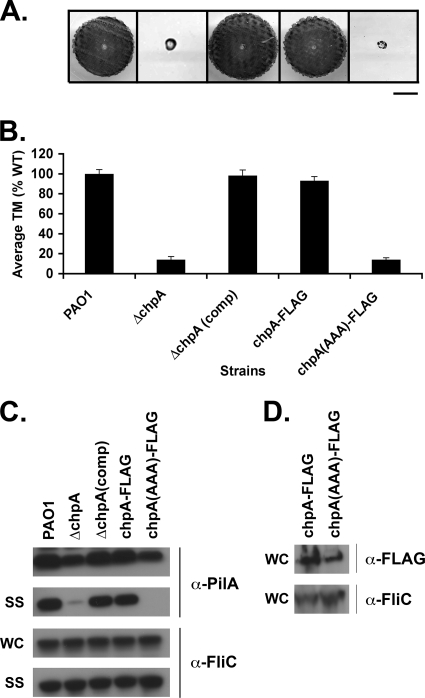
FIG. 7.
The histidine kinase domain of ChpA is required for function. (A) Subsurface TM assay of PAO1 (WT) and the ΔchpA, ΔchpA(comp), and FLAG-tagged chpA (chpA-FLAG) mutants, as well as the FLAG-tagged chpA histidine kinase mutant [chpA(AAA)-FLAG]. Bar, 1 cm. (B) Graph depicting average TM zone diameters for the indicated strains. Shown are the means ± the SD (n = 5). The residual zone of TM in the ChpA mutants represents colony growth and is similar to that of the ΔpilA mutant. (C) Surface structures (SS) and intracellular (WC) preparations of the indicated strains were immunoblotted with a polyclonal antibody to PilA (α-pilA) or to FliC (α-FliC), as described in Fig. 2. (D) Levels of ChpA-FLAG and ChpA(AAA)-FLAG. To prepare protein samples, cells were harvested from 2 ml of culture grown shaking for 16 h at 37°C, resuspended in 400 μl of SDS-PAGE sample buffer, passaged through a 27.5 gauge needle three times, and boiled for 5 min. Then, 10% of the total sample volumes were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with 2.5 μg of α-FLAG M2 monoclonal antibody/ml.