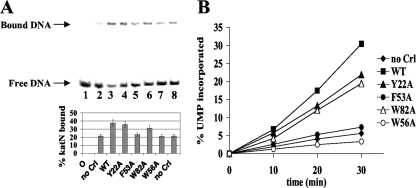
FIG. 7.
Effects of the Crl variants on EσS promoter binding and abortive transcription. (A) Band shift analysis of EσS binding to the katN-labeled fragment in the absence of Crl (lanes 2 and 8) and in the presence of wild-type (WT) Crl (lane 3) or its variants Y22A (lane 4), F53A (lane 5), W82A (lane 6), and W56A (lane 7). Lane 1, no protein. A typical autoradiogram is shown. The bands corresponding to free and bound DNAs are indicated by arrows, and the percentage of bound DNA indicated below each lane is the average of two experiments. (B) Abortive initiation assays. EσS was preincubated in the absence of Crl or in the presence of wild-type Crl or its variants Y22A, F53A, W82A, and W56A. After addition of a mixture containing the lacUV5 fragment, the ApA dinucleotide, and [α-32P]UTP, the incorporation of labeled [α-32P]UMP into abortive transcripts was monitored as a function of time. The measurements were repeated twice, and a representative experiment is shown.