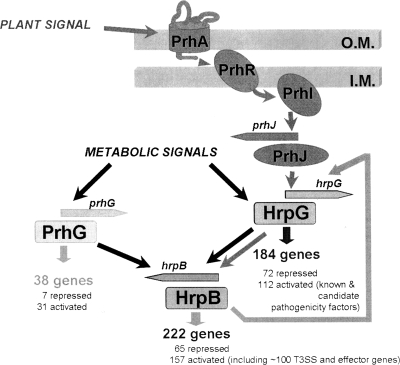
FIG. 7.
Model describing the regulation network involved in the control of R. solanacearum pathogenicity. HrpB is the regulator mainly devoted to the control of the T3SS and effector gene transcription. PrhG and HrpG both regulate the expression of hrpB but belong to different signaling pathways and integrate at least two distinct inducing signals. The nature of the activating plant signal(s) is unknown, but it requires physical contact between bacteria and plant cells (1). The metabolic signals indicated here are those perceived by bacteria grown under minimal medium conditions. HrpG regulates, independently of HrpB, the expression of a subset of genes that includes several virulence and pathogenicity factors (33). The specific subset of genes regulated by PrhG is smaller and contains only one other target regulated by HrpG, RSp0201. The feedback loop by which HrpB induces hrpG (see text) is also shown. O.M., outer membrane; I.M., inner membrane.