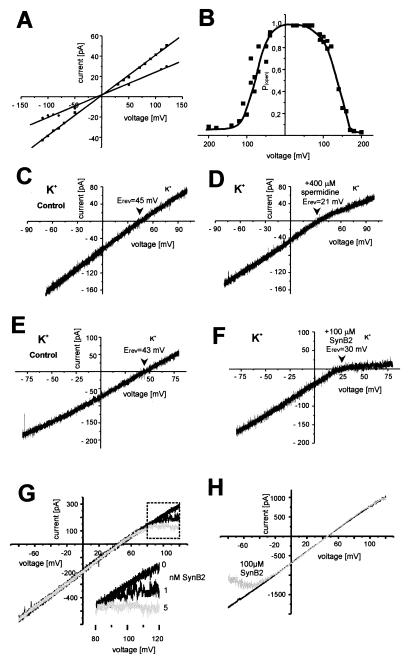
Figure 2.
SynToc75 forms a high conductance cation-selective channel. (A) Current–voltage relationship of the fully open single channel (squares) and the most frequent subconductance level (circles) with 250 mM KCl on both sides of the membrane (data points were averaged from five independent bilayers, with SEMs <3.5%). (B) Voltage dependence of the probability for the SynToc75 channel being in any of its open states. To approach equilibrium of channel gating with respect to the applied membrane, voltages were applied for 5 min, but only the current recordings of the last minute were used to calculate open probability from the amplitude histograms (averages of at least three independent bilayers, with SEMs <6% of the values). (C and D) Influence of SynB2 (MLSRQQSQRQSQQSQRQSRYLL, Mr = 2, 9) and spermidine on the SynToc75 conductivity. Voltage ramps (ΔV = 10 mV/s) were applied across bilayers containing multiple copies of the active SynToc75 channel. (C) Recording from a bilayer containing four active copies of the SynToc75 channel in asymmetrical 250 mM/20 mM KCl, 10 mM Mops/Tris (pH 7.0) buffer (cis/trans), control. (D) Same bilayer as in C, but after addition of 400 μM spermidine to the trans compartment. (E) Recording from a bilayer containing four active copies of the SynToc75 channel in asymmetrical 250 mM/20 mM KCl, 10 mM Mops/Tris (pH 7.0) buffer (cis/trans), control. (F) Same bilayer as in E, but after addition of 100 μM SynB2 to the trans compartment. (G) Recording from a bilayer containing 12 active copies of the SynToc75 channel in asymmetrical 250 mM/20 mM KCl, 10 mM Mops/Tris (pH 7.0) buffer (cis/trans). Black, control; gray/light gray, after addition of 1/5 nM SynB2 respectively to the trans compartment. (H) Recording from a bilayer containing 44 active copies of the SynToc75 channel in asymmetrical 250 mM/20 mM KCl, 10 mM Mops/Tris (pH 7.0) buffer (cis/trans). Black, control; gray, after addition of 100 μM SynB2 to the cis compartment.