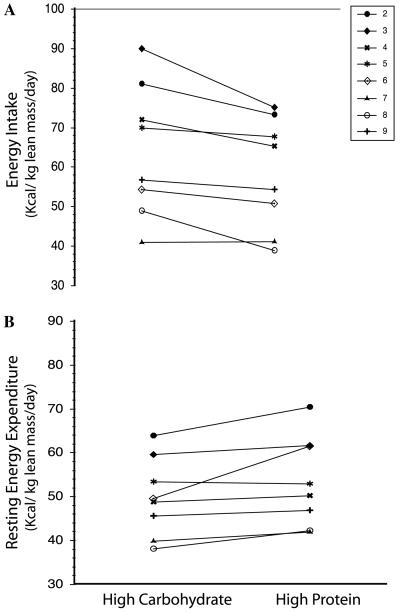
Fig. 1.
Effect of diet on energy intake and resting energy expenditure in subjects with LCHAD or TFP deficiency. (A) Change in daily energy intake (kcals/day) from the high carbohydrate diet phase (High CHO) and the high protein diet phase (High Protein). Energy intake was significantly lower during the high protein diet phase (High CHO 1726 ± 349, High Protein 1676 ± 271, p = 0.021). (B) Change in resting energy expenditure from the high carbohydrate diet phase (High CHO) and the high protein diet phase (High Protein). Resting energy expenditure was significantly higher during the high protein diet phase (High CHO 1398 ± 305 High Protein 1569 ± 329, p=0.05).