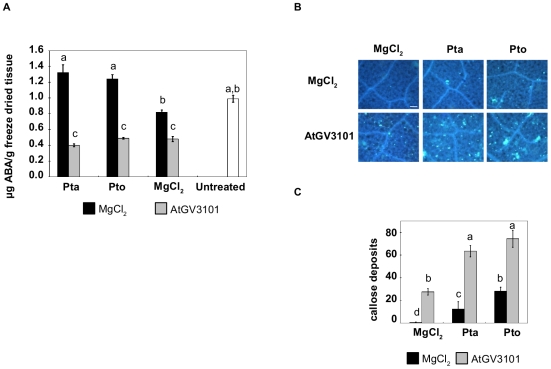
Figure 6. Agroinfiltration decreases ABA levels and primes callose deposition in N. tabacum.
Leaves were inoculated with A. tumefaciens GV3101 (AtGV3101) at 107 cfu/ml or with 10 mM MgCl2(AS), followed 48 hours later by P. syringae pv. tabaci 11528 (Pta) or P. s. pv. tomato DC3000 (Pto) at 105 cfu/ml, or 10 mM MgCl2. A. ABA levels were determined for whole leaf samples by LC/MS/MS. The graphs show average values from five independent experiments. The bars indicate the standard error of the mean. One way ANOVA revealed statistical differences between treatments (F = 11.1058; p<0.0001; df = 6). Means with the same letter were not significantly different at the 5% confidence level based on Student's t-test. B. Leaf sections were excised 24 hours after infiltration with P. syringae, stained with aqueous aniline blue, and imaged under ultraviolet excitation at 370 nm. Pictures are representative of five areas of 1.3 mm2 taken from a leaf section. Two sections from two leaves were stained in each experiment and the experiment was performed twice with similar results. Scale bar, 100 µm. C. Average callose deposits per field of view (1.3 mm2). The bars indicate the standard error of the mean. GLM revealed statistical differences between treatments (F = 58.7652; p<0.0001; df = 5). Means with the same letter were not significantly different at the 5% confidence level based on Tukey's HSD Test.