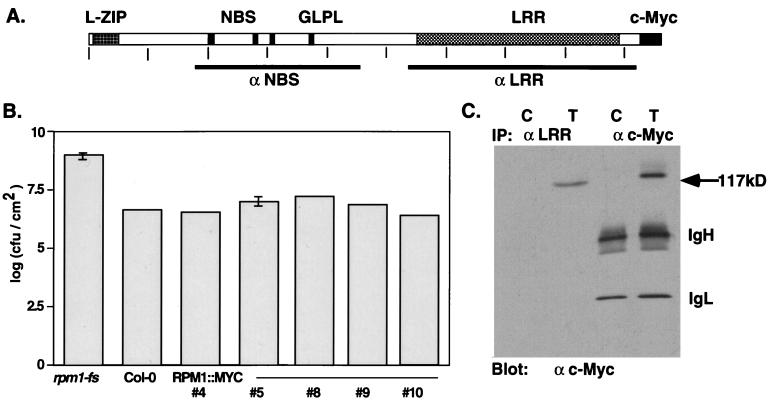
Figure 1.
Structure, function, and immunodetection of RPM1∷MYC. (A) The deduced RPM1 protein indicating the position of the leucine zipper (L-ZIP), putative NBS, and LRR domains. GLPL denotes the core of a conserved sequence motif of unknown function found in all NBS-LRR proteins. Vertical ticks occur every 100 aa. Bars below the schematic define the regions of the protein used to generate the anti-NBS and anti-LRR polyclonal antisera. (B) Complementation of the rpm1-fs mutation with RPM1∷MYC. Bacterial growth in leaves infiltrated with DC3000(avrRpm1) at a density of ≈5.5 × 103 cfu/cm2 was assayed 72 hpi. In planta bacterial titers are given for nontransformed rpm1-fs, wild-type Col-0, and five independent rpm1-fs (RPM1∷MYC) transgenic lines. (C) Immunodetection of RPM1∷MYC by using monoclonal anti-c-Myc antibody after immunoprecipitation with either anti-LRR antisera or monoclonal anti-c-Myc antibody. C is extract from nontransformed control plants, T from transgenic #4 of B. Anti-mouse IgG second step antibody detects the IgG heavy (IgH) and light (IgL) chains of the monoclonal.