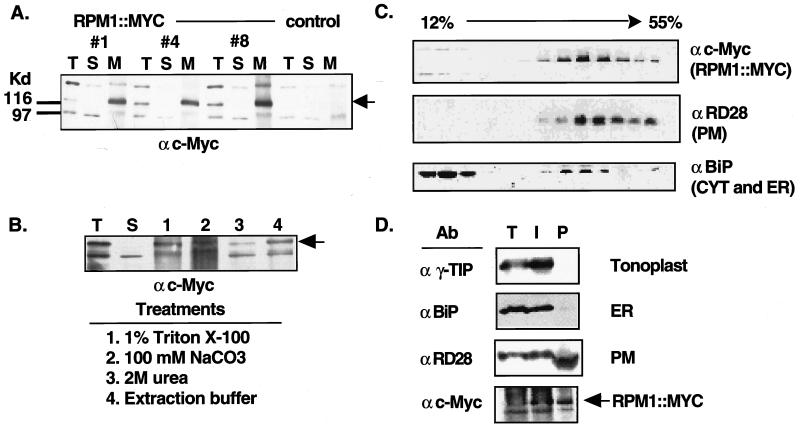
Figure 2.
RPM1∷MYC is a peripheral PM protein. (A) Protein blot of total (T), soluble (S), and microsomal membrane (M) fractions from nontransformed rpm1-fs control plants and three rpm1-fs (RPM1∷MYC) transgenic lines reacted with the anti-c-Myc monoclonal antibody. Equal amounts of protein were loaded in each lane. Arrowhead indicates the position of RPM1∷MYC. Anti-c-Myc crossreacting bands at ≈98 and ≈150 Kd were present in nontransformed control lines. (B) Protein blot reacted with the anti-c-Myc monoclonal antibody demonstrating peripheral association of RPM1∷MYC with the membrane. Total extract (T) was centrifuged at 100,000 × g to generate soluble (S) and microsomal membrane fractions. Membranes were treated as specified to release peripheral membrane proteins. Remaining membranes were pelleted and the newly soluble proteins were analyzed. (C) Fractionation of RPM1∷MYC on sucrose gradients. A 12–55% (wt/vol) linear sucrose gradient was used to fractionate total extract from transgenic plants. Aliquots of each fraction were blotted to nitrocellulose and were analyzed with either anti-c-Myc or the subcellular compartment marker antibodies listed at the right of each panel. (D) Protein blot analysis of membranes fractions obtained by aqueous two-phase partitioning. Total extract (T), intracellular membrane (I), and plasma membrane (P) vesicle fractions were separated by SDS/PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose and reacted sequentially with antibodies against the c-Myc epitope, RD28, γ-TIP, and BiP.