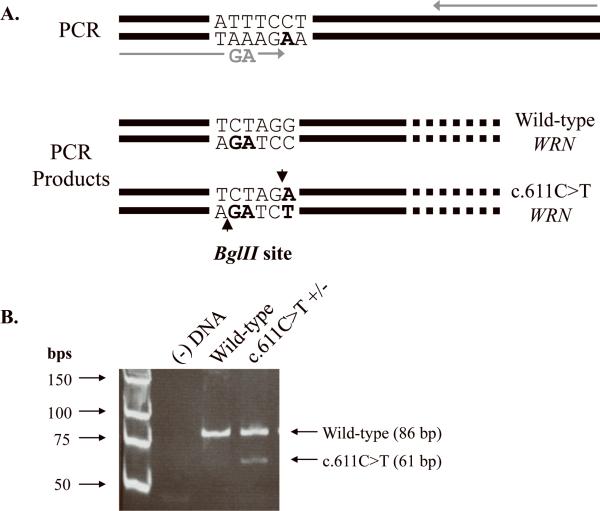
Fig. 3. Screen for the c.611C>T mutation in 199 additional sarcomas.
(A) Schematic of the screen for the c.611C>T mutation in WRN. PCR amplification with mutagenic primers (grey arrows) introduces two nucleotide changes that create a BglII restriction site only if the c.611C>T mutation is present. Amplification of a wild-type sequence with these same primers does not result in an additional cleavable BglII site. (B) PCR amplification results in a 1335 bp product. BglII cleavage of a wild-type product results in two fragments, 1249 bp (not shown) and 86 bp in length (lane 3: wild-type WRN). BglII digestion of amplified DNA, heterozygous for c.611C>T WRN, generates four fragments, 1249 bp (not shown), 86 bp, 61 bp, and 25 bp (not shown), in length (lane 4: c.611C>T WRN). The digestion products were visualized following electrophoresis through a 12% polyacrylamide gel. In order to better resolve the 86 bp and 61 bp products, the smallest 25 bp fragment was electrophoresed off the gel. Lane 1: low molecular weight ladder and lane 2: (−) DNA control.