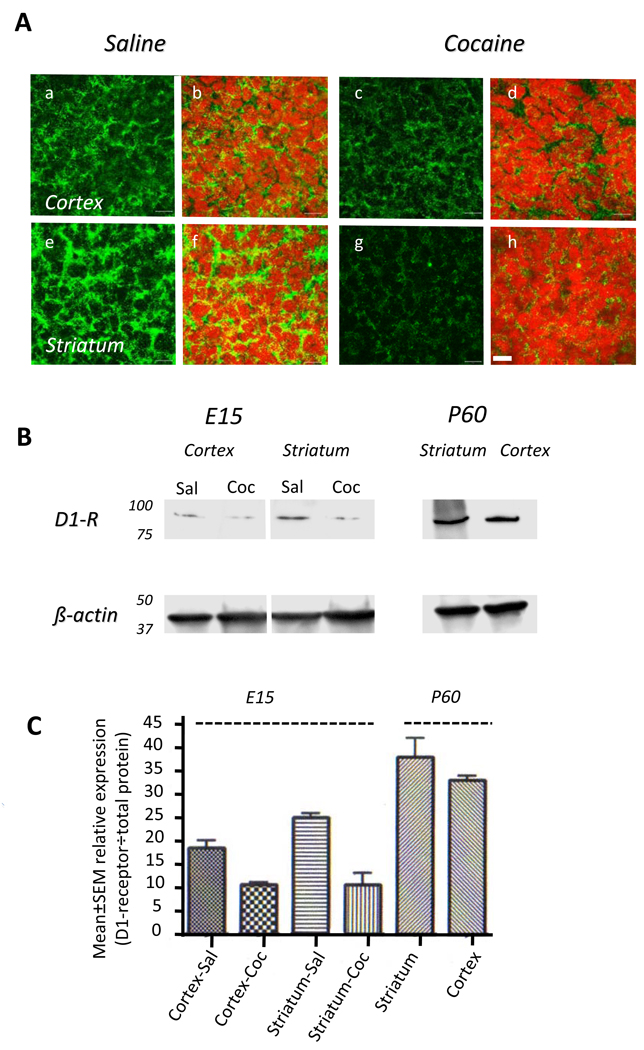
Figure 2.
Dopamine D1-receptor expression in the saline- or cocaine-exposed E15 mouse brain. A. Immunohistochemistry reveals D1-receptor labeling (green) in cryostat sections of the cerebral cortex (a–d) and striatum (e–h). Nuclei are labeled with propidium iodide (red). The D1-receptor immunoreactivity is localized to the cytoplasm and it is significantly reduced in the cocaine exposed cerebral cortex (c,d) and striatum (g,h) compared to the saline exposed cerebral cortex (a,b) and striatum (e,g). B. Western blot reveals reductions in D1-receptor protein in the cerebral cortex and striatal extracts from an E15 cocaine-exposed embryo (Coc) compared to age-matched saline-exposed embryo (Sal). To verify antibody specificity, samples of striatum and cortex from postnatal day 60 (P60) mice were analyzed in parallel experiments. Protein loading was standardized by using β-actin. C. Quantitative analysis of band intensities shows reduced intensities in the cocaine-exposed samples compared to the saline-exposed control samples. The significantly higher expression in the P60 samples compared to the E15 samples is also evident.