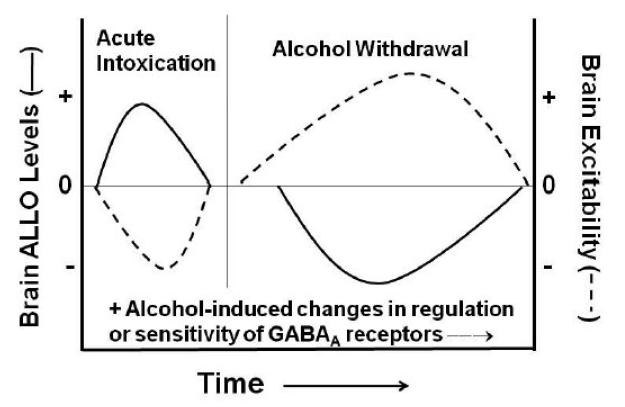
Figure 6. Hypothetical model for interaction of alcohol intoxication- versus alcohol withdrawal-related effects on endogenous ALLO levels and brain excitability.
The effect of acute intoxication or alcohol withdrawal on endogenous ALLO levels is depicted by the solid line, while the subsequent change in brain excitability is depicted by the dashed line. In general, the impact of endogenous neurosteroid tone on GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition exhibits an inverse relationship on brain excitability (i.e., ↑ ALLO = ↓ excitation; ↓ ALLO = ↑ excitation). Disparate influences of alcohol intoxication and withdrawal on ALLO levels, in conjunction with differential alterations in GABAA receptor plasticity within discrete brain regions, likely underly sex differences in the effects of GABAergic neurosteroid manipulations on measures of alcohol self-administration and withdrawal.