Fig. 3.
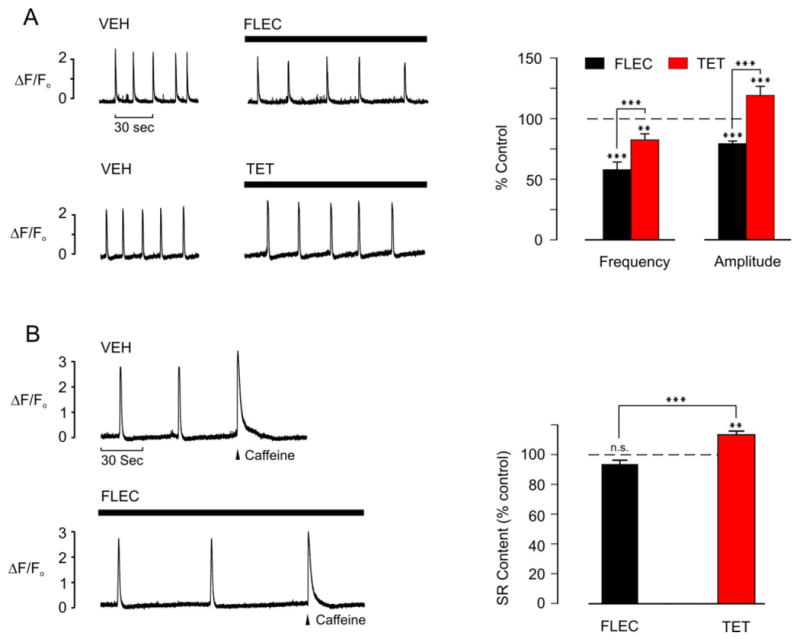
Effects of flecainide or tetracaine on Ca2+ waves and the SR Ca2+ content in permeabilized rat myocytes
(A) Representative integrated line-scan images (left) showing spontaneous Ca2+ waves in permeabilized ventricular myocytes during exposure to vehicle (VEH) and after 2 min exposure to either 25 μM flecainide (FLEC) or 50 μM tetracaine (TET). Average data (right) comparing the effects of flecainide and tetracaine on Ca2+ wave amplitude and frequency. FLEC n = 9, TET n = 7, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
(B) Representative integrated line scan images (left) showing spontaneous Ca2+ waves in permeabilized ventricular myocytes in the presence of vehicle or 2 min after introduction of 25 μM FLEC. In both cases, the wave frequency was monitored and 10 mM caffeine rapidly applied when a wave would otherwise have occurred (arrowhead). The amplitude of the caffeine-induce Ca2+ transient was used as an index of the SR Ca2+ content in each case. Average data comparing the effects of flecainide and tetracaine on the SR Ca2+ content under these conditions (right). FLEC n = 6, TET n = 6, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, n.s. = not significant.
