Figure 6.
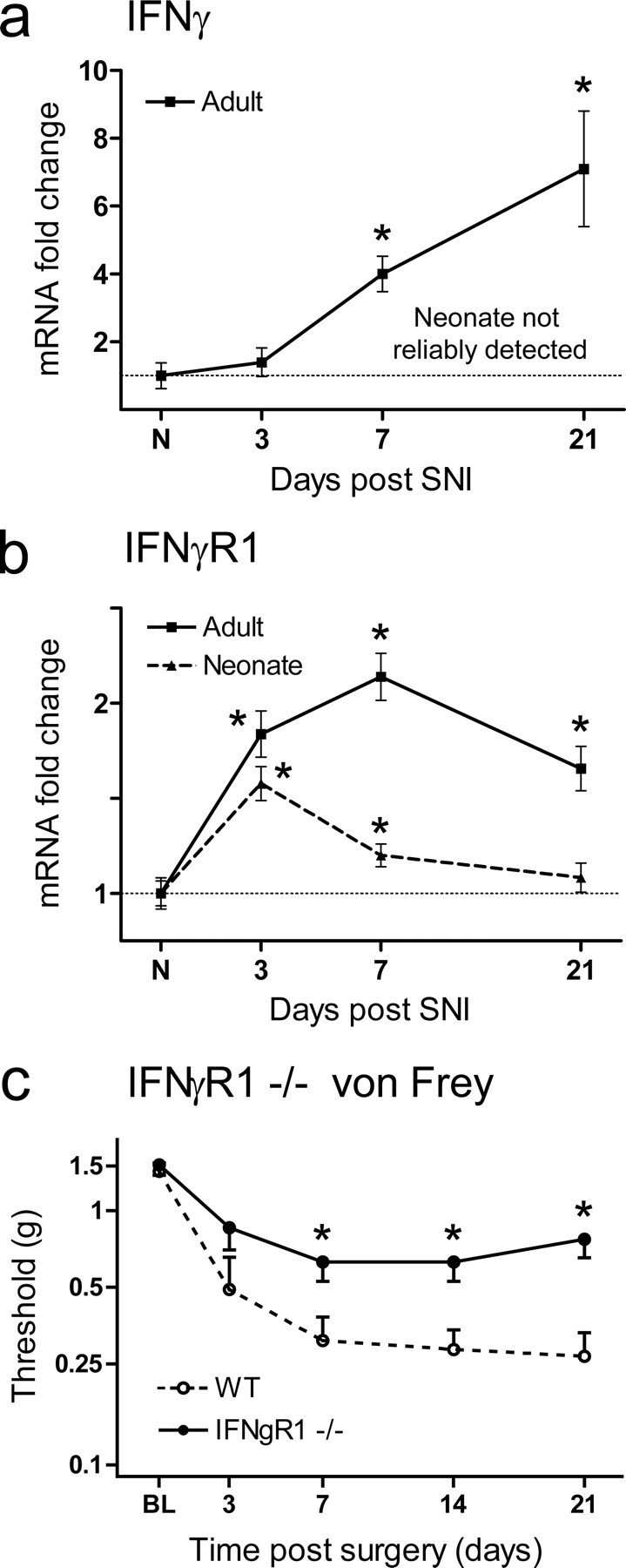
a, Expression analysis of the IFNγ mRNA by quantitative PCR reveals little evidence of expression in the injured or age-matched control neonatal dorsal horn, in contrast to the adult, where IFNγ mRNA increases successively over time. b, IFNγR1 mRNA is upregulated in the neonatal and adult dorsal horn over time after SNI; levels of regulation are, however, considerably reduced in the neonate relative to the adult. Data are expressed as mean fold ± SEM. *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA, Student's t test, n = 4 per group. c, Mechanical sensitivity over time subsequent to SNI injury in IFNγR1-null animals and wild-type littermate control mice. IFNγR1-null animals display less mechanical allodynia relative to controls. All data are mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA (time and genotype) for genotype (F(1,4) = 10.32; p < 0.05; post hoc Student's t test, *p < 0.05, n = 7 animals per group).
