Table 2. Most negatively correlated mRNAs and miRNAs.
| mRNAs | |||||||
| RefSeq ID | Gene ID | Gene Symbol | mean | n | rand | p |
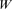
|
| NM_014810 | 9857 | CEP350 |

|
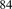
|

|

|

|
| NM_003012 | 6422 | SFRP1 |
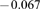
|

|
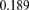
|

|

|
| NM_052854 | 90993 | CREB3L1 |
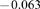
|

|

|

|

|
| NM_006499 | 3964 | LGALS8 |

|

|

|
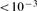
|

|
| NM_201543 |

|

|
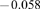
|

|

|
||
| NM_000517 | 3040 | HBA2 |

|

|

|
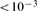
|

|
| NM_000558 | 3039 | HBA1 |
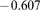
|
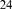
|

|
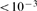
|
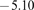
|
| NM_004305 | 274 | BIN1 |

|

|
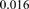
|

|
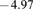
|
| NM_000873 | 3384 | ICAM2 |

|

|
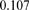
|

|
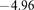
|
| NM_001008540 | 7852 | CXCR4 |

|

|

|

|

|
The ten mRNAs most negatively correlated with their regulating miRNAs, and ten miRNAs most negatively correlated with their target mRNAs, as measured by their weighted correlation shift (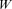 ). Repeated mRNAs (RefSeq IDs that map to the same UTR and therefore the same probesets and same expression) were removed from the table. Data was limited to mRNAs with log-expression values greater than 4. Header legend:
mean: mean correlation over all targets (in the case of miRNAs) or regulators (in the case of mRNAs); n: number of correlations included in the mean. rand: average correlation after randomization.
). Repeated mRNAs (RefSeq IDs that map to the same UTR and therefore the same probesets and same expression) were removed from the table. Data was limited to mRNAs with log-expression values greater than 4. Header legend:
mean: mean correlation over all targets (in the case of miRNAs) or regulators (in the case of mRNAs); n: number of correlations included in the mean. rand: average correlation after randomization.
