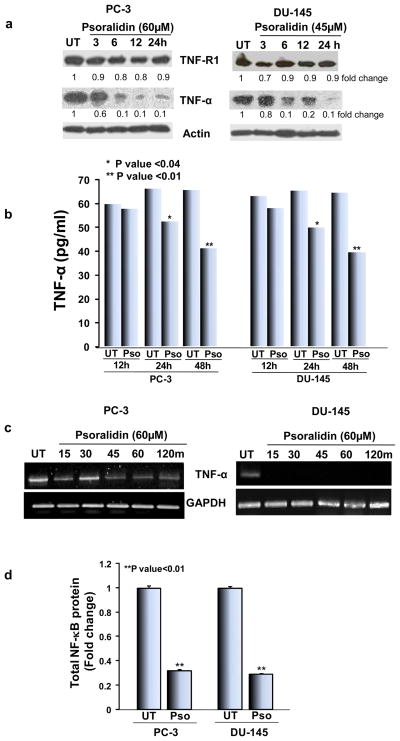
Figure 1. Effect of psoralidin on TNF-α and NF-κB in AIPC cells.
(A) PC-3 and DU-145 cells (70–80% confluency) were treated with 60 and 45 μM psoralidin, respectively, for varying time intervals (3–24 h), and Western blot analysis was performed using TNF-α and TNF-R1 antibodies. Actin was used as the internal loading control. (B) PC-3 and DU-145 cells (70–80% confluency) were treated with 60 and 45 μM psoralidin, respectively, for 12, 24 or 48 h, and the supernatant was collected after the treatment periods, protein concentration in the supernatant was quantified and equal amounts of protein were subjected to sandwich ELISA for quantitation of secreted TNF-α levels in control and psoralidin-treated AIPC cells. (C) PC-3 and DU-145 cells (70–80% confluency) were treated with 60 and 45 μM psoralidin, respectively, for varying time intervals (3-2 h), and total RNA was isolated using Trizol method, cDNA was synthesized using two step RT-PCR and TNF-α mRNA expression was determined. (D). PC-3 and DU-145 cells (70–80% confluency) were treated with 60 and 45 μM psoralidin, respectively, and cell lysates were subjected to sandwich ELISA for quantitation of total NF-κB protein levels in control and psoralidin-treated AIPC cells. Bars represent mean±SD.