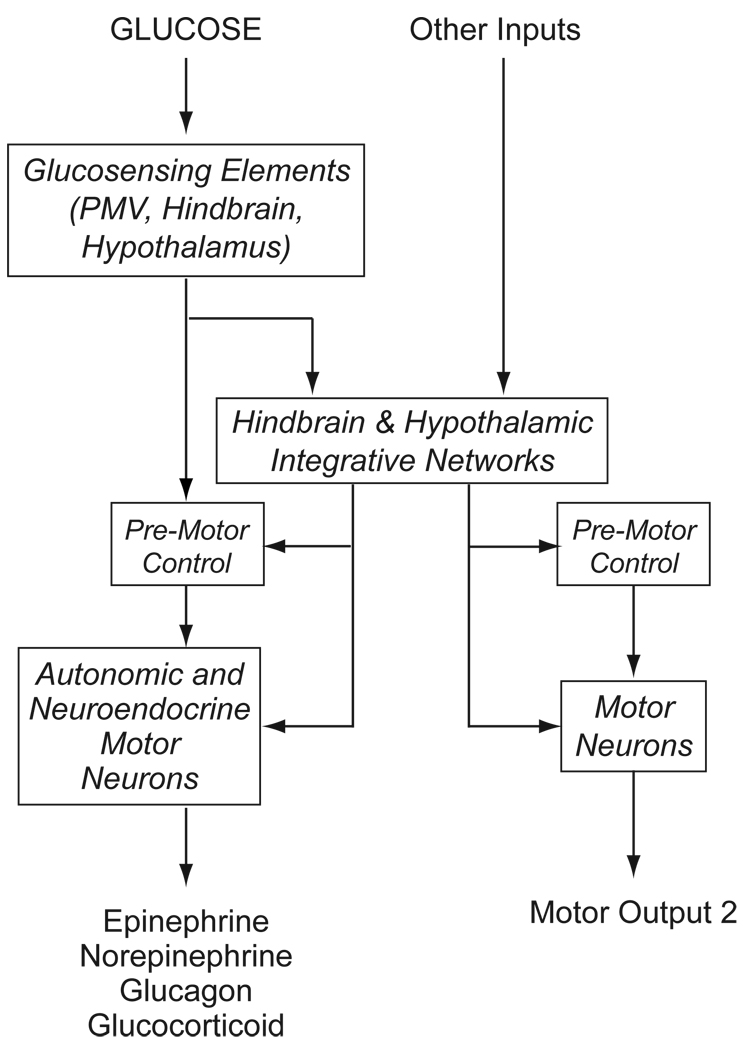
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram to illustrate how glucose, acting as an interosensory stimulus engages glucosensing elements that transduce information into neural signals that control hypoglycemic counterregulation. Consistent with classic sensorimotor integration, these signals use neural pathways to engage either premotor control networks to drive autonomic and neuroendocrine motor neurons in a reflex manner; or more complex integrative networks in the hypothalamus and hindbrain. These integrative networks allow glucosensation to be integrated with other information that can modulate counterregulatory responses, as well as providing a way for glucosensation to influence other motor process, such as those that control reproductive behavior.