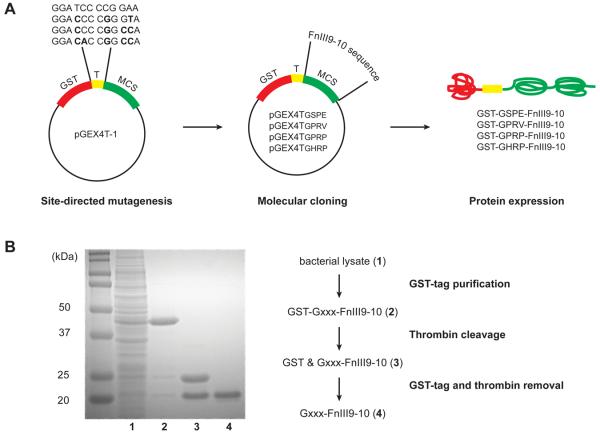
Fig. 2.
Gxxx-FnIII9-10 protein production and purification. (A) Molecular engineering of the pGEX4T-1 vector to express proteins with variable thrombin cleavage sites, LVPR↓Gxxx. Site-directed mutagenesis was used to modify the coding sequence for the thrombin cleavage site (T). Next, the open reading frame of the protein-of-interest, FnIII9-10, was inserted into the multiple cloning site (MCS). The expressed proteins comprise an N-terminal glutathione S-transferase (GST) tag, followed by the thrombin cleavage site and protein-of-interest. (B) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel demonstrating protein purity at the different stages of purification using affinity chromatography. GST-tagged Gxxx-FnIII9-10 (lane 2) was purified from contaminating proteins in the bacterial cell lysate (lane 1) via the GST affinity column. Thrombin-catalyzed cleavage releases the 26 kDa GST-tag from the 20 kDa Gxxx-FnIII9-10 protein (lane 3). Next, the thrombin and GST-tag were removed using benzamidine and GST affinity columns respectively, leaving the desired protein-of-interest (lane 4).