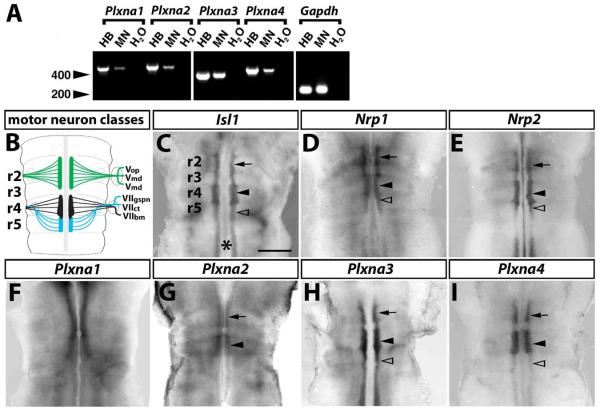
Fig. 1. A-type plexin expression in motor neurons.
(A) RT-PCR analysis of mouse hindbrain tissue (HB), primary rat embryonic motor neurons (MN) and a negative control (H2O) for Plxna1-a4 and a Gapdh control; molecular weight marker: 200 and 400 bp (arrowheads). (B) Motor neuron populations in the mouse hindbrain at 10.5 dpc; r2-derived neurons are shown in green, r4-derived neurons in black and r5-derived neurons in blue; abbreviations: VOP, VMX, VMD - ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular branches of the Vth cranial (trigeminal) nerve; VIIGSPN, VIICT, VIIBM - greater superficial petrosal nerve, chorda tympani and branchiomotor nerve of the VIIth cranial (facial) nerve. (C-I) Wholemount in situ hybridisation of 10.5 dpc mouse hindbrains. (C) A probe specific for the motor neuron marker Isl1 reveals the nascent motor neuron column on each side of the midline (asterisk); focal thickenings at the level of r2 and r4 contain the trigeminal (arrow) and facial branchiomotor neurons (black arrowhead), respectively. Facial visceromotor neurons are born in r5 (clear arrowhead); r5 also contains caudally migrating facial branchiomotor neurons. (D,E) Hindbrain motor neurons express Nrp1 (D) and Nrp2 (E). Plxna1 is expressed near the midline in all rhombomeres anterior to r5 (F); the expression patterns of Plxna2 (G), Plxna3 (H) and Plxna4 (I) are consistent with a role in trigeminal (arrow) and facial (arrowhead) branchiomotor neurons; Plxna3 (H) and Plxna4 (I) are also expressed in posterior hindbrain motor neurons, including those in r5 (clear arrowhead). Scale bar (C-I): 500 μm.