Fig. 2.
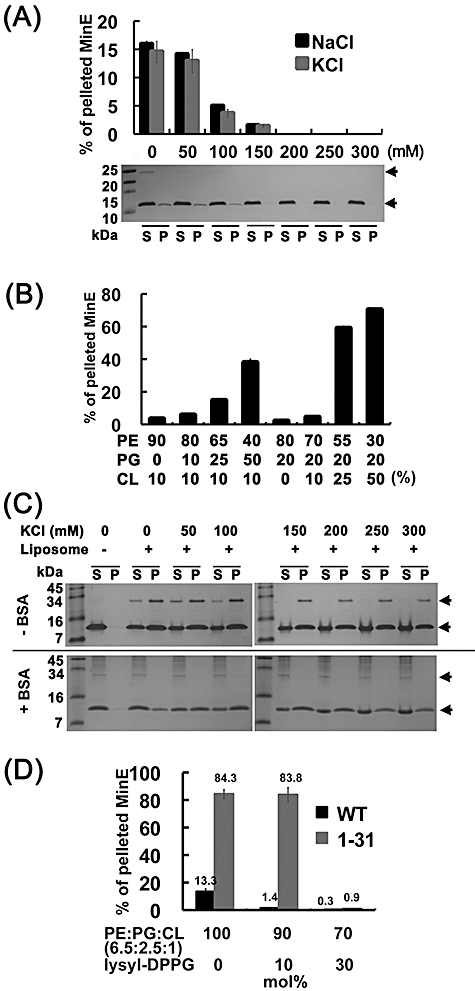
Electrostatic force is involved in mediating the MinE–membrane interaction. A. The co-sedimentation of full-length MinE with liposomes was disrupted by increasing concentrations of NaCl and KCl. The Tris-Tricine-SDS gel image exemplified an experiment with different NaCl concentrations that were used in the analyses. The lower arrow indicates the position of MinE. The higher arrow indicates an additional 28 kDa band induced by the presence of liposomes. S, supernatant; P, pellet. B. MinE showed a binding preference for the anionic phospholipids PG and CL. C. The MinE–membrane interaction was stabilized under high salt conditions by the presence of 50 mol% cardiolipin (PE : PG : CL = 36:14:50). The lower and higher panels show experiments with or without the presence of 18 µM BSA respectively. MinE was supplied at 6 µM in these reactions. Note that the 28 kDa band was relocated to the supernatant fraction in the presence of BSA, indicating its appearance in the pellet fraction was mostly non-specific. The additional bands in the lower gel were impurities of the BSA solution. D. Addition of cationic lysyl-DPPG to liposomes interfered with the co-sedimentation of MinE and MinE1–31 with liposomes. The reactions were incubated for 60 min prior to centrifugation.
