Figure 2.
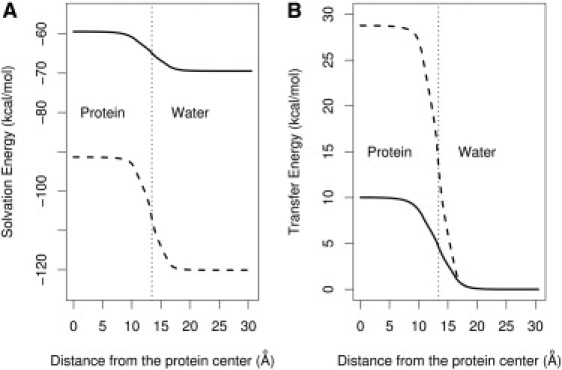
Comparison of solvation and transfer free energies between the LD model (solid line) and the Born model (dashed line). (A) The electrostatic solvation energy calculated for a dipole composed of two unit charges of opposite sign and with a fixed length of 3 Å placed at various positions in the protein-water system. (B) The transfer free energy required to move the dipole from water into the interior of the protein, calculated by subtracting the baseline from the two curves in A. The protein is spherical, with a radius of 13.4 Å, which corresponds to the radius of gyration of a 100-residue globular protein. The dotted vertical line denotes the position of the boundary between the spherical protein and water.
