Figure 2.
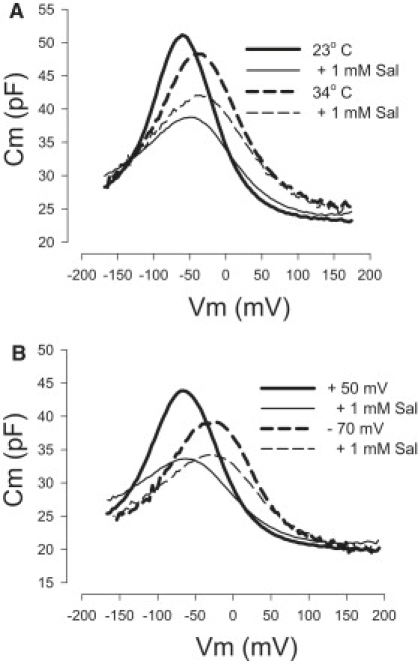
Competition between salicylate and chloride for prestin's anion-binding site is dependent on temperature and holding voltage. (A) A representative OHC was whole-cell patched with 140 mM Cl− in and out, and perfused with 1 mM salicylate first at 23°C (solid lines) and then at 34°C (dashed lines). The reduction of NLC after salicylate perfusion (thin lines) is less under the high-temperature condition. Average reductions of nonlinear peak capacitance for salicylate treatment are 9.9 ± 1.00 pF (mean ± SE) vs. 5.58 ± 0.73 pF (mean ± SE) (n = 4, P < 0.05, paired t-test). (B) A representative OHC was whole-cell patched and perfused with 1 mM salicylate at room temperature. The OHC was held at either −70 mV (dashed lines) or + 50 mV (solid lines). The reduction of NLC after salicylate perfusion (thin lines) is less at the −70 mV holding potential. The average reduction of nonlinear peak capacitance for salicylate treatment is 10.50 ± 0.16 (mean ± SE) at positive holding potentials and 6.41 ± 1.05 (mean ± SE) at negative holding potentials (n = 4, P < 0.005, paired t-test).
