FIGURE 8.
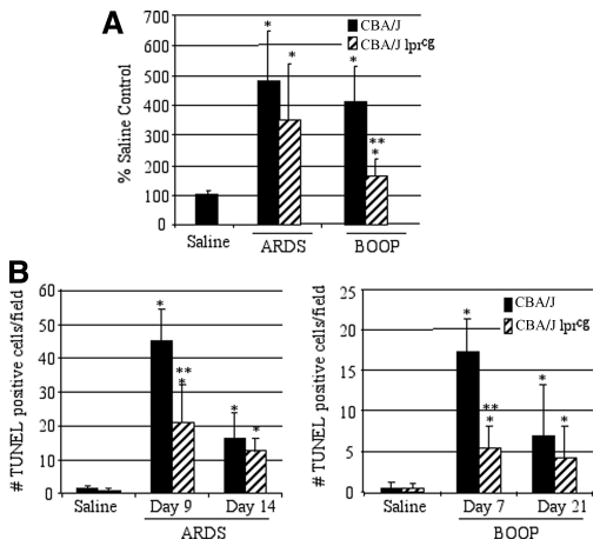
Apoptosis is reduced in reovirus 1/L-inoculated CBA/K1Jms-Faslpr-cg/J mice. CBA/J or CBA/KlJms-Faslpr-cg/J mice were i.n. inoculated with either 1 × 106 PFU (BOOP) or 1 × 107 PFU (ARDS) reovirus 1/L and sacrificed at the indicated time points. A, Sirius red staining in both CBA/J or CBA/KlJms-Faslpr-cg/J mice was quantitated in reovirus 1/L-induced ARDS (day 14) and in reovirus 1/L-induced BOOP (day 21) using ImageJ software. Results are expressed as the percentage of Sirius red content in saline-inoculated, control mice. Sirius red data represent mean ± SD of two experiments with two mice per time point. *, p < 0.05 compared with saline-inoculated, control mice. **, p < 0.05 compared with reovirus 1/L-inoculated mice. B, Apoptosis in situ was assessed using TUNEL labeling on paraffin-embedded lung sections. TUNEL-positive cells in saline (day 9 ARDS; day 7 BOOP) and in reovirus 1/L-induced ARDS on days 9 and 14 or in reovirus 1/L-induced BOOP on days 7 and 21 are shown. TUNEL data represent mean ± SD of eight 225-mm2 fields from two experiments with two mice per time point. *, p < 0.05 compared with saline-inoculated, control mice; **, p < 0.05 compared with reovirus 1/L-inoculated mice.
