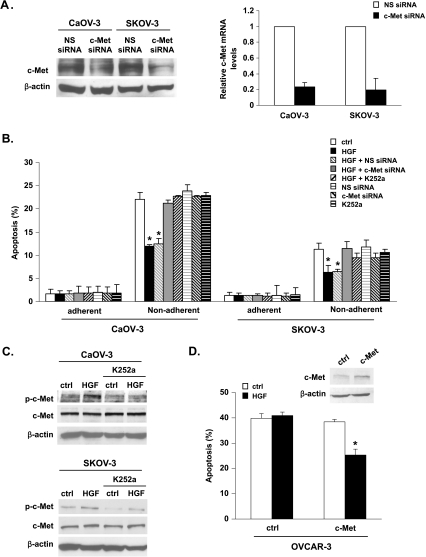
Figure 2.
Effects of c-Met silencing on anchorage-independent growth and anoikis resistance. CaOV-3 and SKOV-3 cells plated on culture dishes (adherent) or polyHEMA-coated dishes (nonadherent) were transfected with 10 nM nonspecific (NS) siRNA or c-Met siRNA for 24 hours. (A) Equal amounts of protein (20 µg) were analyzed by Western blot using c-Met-specific antibodies. β-Actin was included as a loading control. Right panel: Total RNA was isolated, and real-time PCR was performed with c-Met and GAPDH sequence-specific primers. The amount of c-Met messenger RNA was normalized for the GAPDH present. (B) Cells were transfected with NS siRNA or c-Met siRNA for 24 hours or pretreated with K252a inhibitor for 30 minutes and then treated with HGF (10 ng/ml) for 72 hours. Cell apoptosis was determined with the TUNEL assay. (C) Twenty micrograms of protein was analyzed by Western blot using phospho (p)-c-Met-specific antibodies. The same membranes were stripped and reprobed with antibodies to c-Met. β-Actin was included as a loading control. (D) OVCAR-3 cells were transfected with empty vector (control) or human c-Met cDNA for 72 hours. Cells were analyzed for c-Met expression by Western blot analysis (inset) or were subjected to TUNEL assay. The number of apoptotic cells was counted, and the bar diagram summarized the percentage of apoptotic cells from triplicate determination. Error bars indicate the SD of the mean. *P < .05 versus untreated controls.