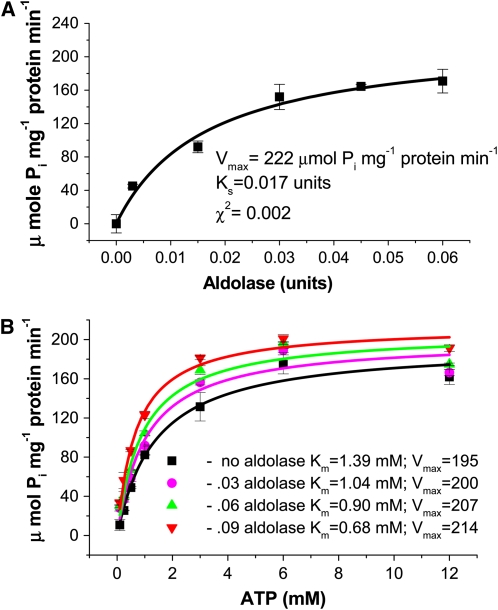
Figure 6.
Aldolase Stimulates V-ATPase Hydrolytic Activity by Increasing Affinity for ATP.
(A) V-ATPase hydrolytic activity (bafilomycin-sensitive and azide- and vanadate-insensitive) was estimated by spectrophotometric measurement of inorganic phosphate release as described in Methods. Activity was measured in tonoplast vesicles (15 μg protein) isolated from M. crystallinum over a range of aldolase concentrations. Data represent means ± se of three replicate experiments. Each replicate experiment was performed using independent membrane preparations. The solid lines show the fit of the kinetic data with the Michaelis-Menten equation, and from this the rate constants Ks and Vmax were calculated. Ks refers to the concentration of aldolase that gives half the maximal velocity, and Vmax refers to the velocity of the enzyme catalyzed reaction at saturating aldolase concentrations. The χ2 value indicates the goodness of fit and confirmed that the data fitted the equation at a probability level of at least P < 0.01.
(B) V-ATPase hydrolytic activity was measured over a range of ATP concentrations in the presence of increasing amounts of aldolase. Data represent means ± se of three replicate experiments performed using independent membrane preparations. The solid lines show the fit of the data with the Michaelis-Menten equation. Units for Vmax are μmol Pi mg−1 protein min−1. The χ2 values, indicating the goodness of fit of the data to the equation, gave probabilities of at least P < 0.05.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]