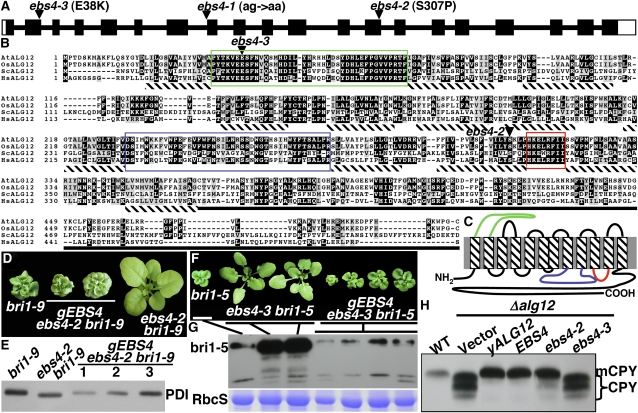
Figure 6.
EBS4 Is the likely Arabidopsis Ortholog of the Yeast ALG12.
(A) Schematic presentation of EBS4 gene structure. Black bars denote exons, with open bars denoting untranslated regions, and the thin lines represent introns. The positions and molecular nature of the three ebs4 mutations are indicated.
(B) Sequence alignment of EBS4 with the yeast ALG12 and ALG12 homologs of rice and human. Alignment of EBS4 (accession number NP_001077448) with the yeast ALG12 (ScALG12, NP_014427) and ALG12 homologs from rice (OsALG12, NP_001053463) and human (HsALG12, NP_077010) was performed at the Tcoffee server (http://tcoffee.vital-it.ch/cgi-bin/Tcoffee/tcoffee_cgi/index.cgi). Identical residues in ≥3 sequences are shaded black, while similar residues are shaded in gray using the BoxShade server at http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html. Two largest loops and a highly conserved cytoplasmic loop are color-boxed, and potential transmembrane domains are underlined with hatched bars. Triangles indicate the residues mutated in ebs4-2 and ebs4-3.
(C) EBS4 contains 12 predicted transmembrane segments. Prediction of potential transmembrane domains was performed at the DAS server (http://www.sbc.su.se/∼miklos/DAS/) and was later adjusted based on the predicted topology of other ALG12 homologs (Oriol et al., 2002). The two largest loops and the highly conserved 5th cytoplasmic loop are shown in colors corresponding to the boxes in (B).
(D) Four-week-old soil-grown plants of bri1-9, ebs4-2 bri1-9, and two EBS4-complemented ebs4-2 bri1-9 transgenic lines carrying a genomic EBS4 transgene (gEBS4) that contains its native promoter and 3′-terminator.
(E) Immunoblot analysis of a PDI in bri1-9, ebs4-2 bri1-9, and three independent gEBS4-complemented ebs4-2 bri1-9 lines.
(F) Three-week-old soil-grown plants of one bri1-5 mutant, two ebs4-3 bri1-5 mutants, and four independent gEBS4-rescued ebs4-3 bri1-5 transgenic lines.
(G) Immunoblot analysis of bri1-5 abundance in plants shown in (F). For both (E) and (G), equal amounts of total proteins extracted in 1× SDS sample buffer from 3-week-old seedlings were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblots using anti-PDI (E) or anti-BRI1 (G) antibody. Coomassie blue staining of RbcS serves as a loading control (G).
(H) Immunoblot analysis of CPY glycosylation in wild-type or transformed Δalg12 yeast cells containing the vector plasmid, the yeast ALG12 gene, the wild-type EBS4, or a mutated EBS4 gene carrying the ebs4-2 or ebs4-3 mutation. See Methods for experimental details.