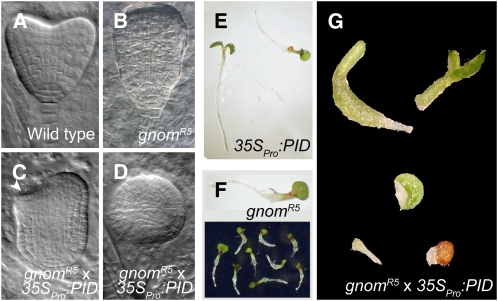
Figure 3.
Genetic Interaction of PID and GNOM.
(A) to (D) Patterning defects in mutant embryos compared with wild-type embryos (A). Apical and basal patterning defects in gnomR5 mutant embryos (B). More severe apical-to-basal embryonic patterning defects in 35SPro:PID gnomR5 double mutants (C), sometimes leading to the complete loss of apical basal patterning (D).
(E) and (F) Viable 35SPro:PID (E) and gnomR5 (F) seedlings.
(G) Strongly affected seedling morphology and growth arrest in 35SPro:PID gnomR5 double mutants, resembling full gnom knockout mutants.