Fig. 3.
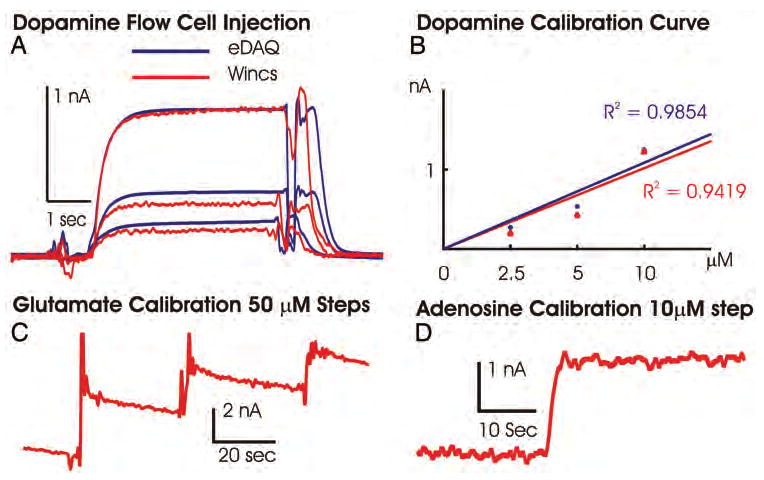
A: Chart showing data obtained after 5-second-long bolus injections of 2.5, 5, and 10 μM dopamine across a single CFM in the flow cell, measured with the WINCS (red line) and a hardwired potentiostat system (eDAQ, blue line). B: Plot of dopamine oxidation current versus dopamine concentrations and linear regression analysis for both FPA recordings made using the WINCS and the eDAQ system. The perturbations in the amperometric signals occurring at the start and end of the 5-second bolus injections of dopamine are a result of engaging and disengaging the electronic valve and do not interfere with the calibration assessments. C: The WINCS glutamate sensor calibration, oxidation current for three 50-μM glutamate concentration steps. D: Calibration of adenosine biosensor performed with a single 10-μM concentration step, as measured with the WINCS.
