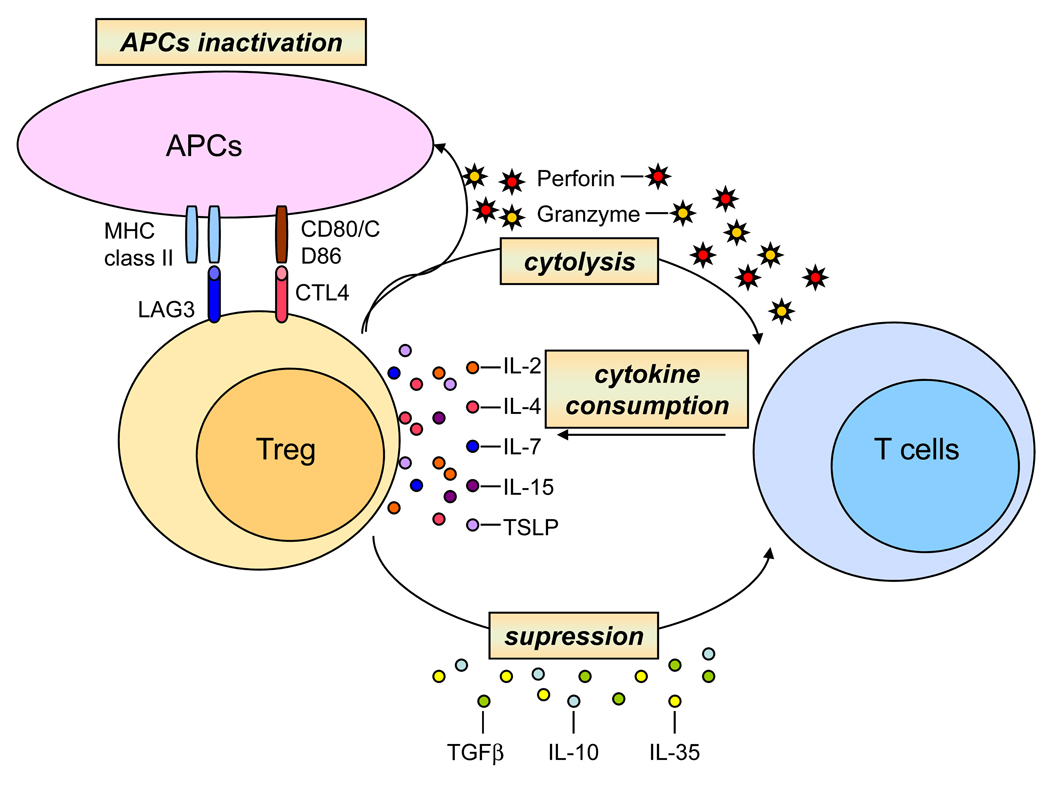
Figure 3. Mechanisms of T cell regulation by Treg cells.
Treg cells exhibit several mechanisms to suppress activation and expansion of conventional T cells. Treg cells modulate functions of APCs by inhibiting their maturation and blocking of MHC molecules and co-stimulatory molecules (CD80 and CD86) on the surface of APCs and thus attenuating interactions between APCs and T cells. Treg cells might have cytolytic effects on target T cells as well as on APCs. Treg cells suppress activation and proliferation of T cells by their secretion of inhibitory cytokines, such as TGFβ, IL-10, and IL-35 and by consumption of γc cytokines. Deprivation of γc cytokines induces expression of pro-apoptotic proteins and elevates apoptotic rate of conventional T cells.