Abstract
Purpose:
To understand ophthalmologists’ current perceptions and treatment of patients with moderate to severe dry eye syndrome (DED).
Methods:
An online survey was distributed to 7,882 ophthalmologists, including 51 corneal specialists, throughout the United States from October 9 to 21, 2008. The response rate was 3.1% (n = 245), typical for this type of survey. Those who treated 4 or more patients with moderate to severe DED per month (235 of 245 [96%]) were asked to complete the survey.
Results:
Ninety-four percent of respondents agreed that more treatment options are needed for moderate to severe DED. Corneal specialists were more likely to strongly agree (63%) than general ophthalmologists (54%). Only 33% overall felt that current therapies were extremely or very effective for moderate DED, and only 5% for severe disease. Ninety-two percent agreed that multiple therapeutic agents are needed to manage moderate to severe DED. The respondents reported prescribing, recommending, or suggesting a mean of 3.2 different treatment approaches over the course of a year for patients with moderate DED and 4.9 for patients with severe DED. The most highly ranked goals in treatment of moderate to severe DED were maintaining and protecting the ocular surface (ranked 1 or 2 by 74%) and lubricating and hydrating the ocular surface (ranked 1 or 2 by 67%). Corneal specialists ranked maintaining and protecting the ocular surface even higher (ranked 1 or 2 by 82%).
Conclusions:
Results reflected the difficulty of treating more serious moderate to severe cases, the importance of using multiple treatment approaches, the limitations of current treatment options, and the need for additional treatment options.
INTRODUCTION
Dry eye syndrome (DED) is characterized by one or more of the following symptoms: burning, itching, foreign body sensation, soreness, dryness, photophobia, redness, and reduced visual acuity.1,2 The tear film instability of DED, which is accompanied by increased osmolarity of the tear film, causes inflammation and structural damage to the ocular surface.1
Dry eye syndrome is a common clinical problem affecting approximately 1 in 3 patients who seek treatment from an ophthalmologist.2 Approximately 5 million Americans aged 50 years and older have DED, and twofold more women than men. In our aging population, the number of people with DED can be expected to increase dramatically.3
Although DED affects all aspects of a patient’s work, leisure, and social life, it poses a challenge to the clinician who must diagnose and treat this disorder. There is a lack of correlation between patients’ symptoms and the results of clinical tests as well as inter-and intra-person variability in the disease process and its symptoms. Repeatable, reliable tests are unavailable,3 and there is variability in responses to questions about the physical sensations in the eyes, along with observer bias in recording slit-lamp findings.3 This has led to a difficult dilemma: some patients may present with ocular damage but no or few symptoms of DED.2
A panel of questions was presented to practicing ophthalmologists throughout the United States to determine their perceptions of moderate to severe DED and how it is treated, and to identify areas of unmet therapeutic need for this disease.
METHODS
Survey questions (see Appendix) assessing participant demographics, perceptions of moderate to severe DED, DED treatment goals, DED therapeutic characteristics, measures of therapeutic success, and potential treatment gaps in DED were sent to 7,882 of the approximately 23,000 practicing ophthalmologists in the United States. Target ophthalmologists, who specialize in corneal/external eye disease, were identified by combining a pool of prespecified e-mail addresses with a list of subscribers to Ophthalmology Times. Prospective participants were sent an e-mail with a Web link to the online survey. To encourage participation in the survey, respondents were enrolled in a drawing to win a single prize of moderate value. No product was mentioned in either the invitation or the survey. Responses were collected from October 9 to 21, 2008, and were summarized in frequency tables organized by query. No comparative analyses were anticipated or utilized in this survey. An institutional review board waiver was provided to conduct this survey.
RESULTS
RESPONDENT DEMOGRAPHICS
Of 7,882 targeted ophthalmologists, 245 (3.1%) submitted completed surveys. Of the participants, the majority (73.9%; n = 181) were male, 21.2% (n = 52) were female, and 4.9% (n = 12) did not specify their gender. Respondents represented all regions of the United States: the Northeast (25.3%; n = 62), the Southwest (22.0%; n = 54), the Southeast (20.0%; n = 49), the Midwest (19.6%; n = 48), the Northwest (2.0%; n = 5), and other regions of the United States, including Puerto Rico (1.6%; n = 4). Ten respondents (4.1%) were from outside the United States, and 13 (5.3%) did not specify their location.
Respondents spent an average of 17.4 years in practice. The majority of participants (66.1%; n = 154) had been in practice for more than 10 years. Most respondents indicated that they were comprehensive ophthalmologists (66.2%; n = 153), and 22.1% (n = 51) stated that they were corneal specialists. Twenty-seven (11.7%) indicated that they were involved in another specialty, and 5.7% (n = 14) did not provide a response to this query. On average, participants reported that they see 112.4 patients per week; of these, approximately 1 in 5 (n = 23.1) are patients with mild, moderate, or severe DED. Respondents who treat fewer than 4 moderate to severe DED patients per week (<4% of total respondents) were not included in the analysis of subsequent responses.
PERCEIVED CAUSES OF DRY EYE SYNDROME
Respondents were asked to indicate by percentage range the primary cause of DED among their patients with moderate to severe disease. Participants could select more than one category as a primary cause; results presented are not cumulative. Listed primary causes included Sjögren syndrome or other autoimmune disease, environmental conditions, postmenopausal hormonal changes, laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) or other ocular surgery, contact lens use, use of systemic medications, and eye/eyelid injury or conditions. Participants were permitted to write in another primary cause of DED if it was not included in the list provided. Respondents indicated that environmental factors and postmenopausal hormonal changes are the most common primary causes of moderate to severe DED in their patients, affecting an average of 36.2% and 34.3%, respectively (Figure 1). Participants indicated that use of systemic medications (21.3%), contact lens use (20.7%), eye/eyelid injury or conditions (19.7%), Sjögren syndrome or other autoimmune disease (18.9%), and LASIK or other ocular surgery (17.3%) were also primary causes of DED in their patients.
FIGURE 1.
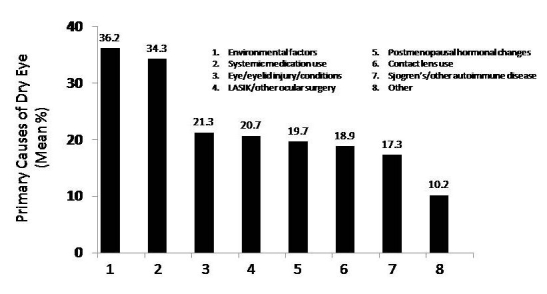
Primary causes of moderate to severe dry eye syndrome expressed as mean percentage of total responses. “Don’t know” responses were excluded from mean calculations.
Survey participants were also asked to indicate if they believed inflammation is the underlying cause of DED, or whether it is merely a consequence of the disease. The majority of respondents (68.6%; n = 168) indicated that inflammation is the underlying cause of DED, whereas 26.1% (n = 64) felt that inflammation is a consequence of the disease. Thirteen participants (5.3%) did not provide an answer to this question.
TREATMENT GOALS AND THERAPY OF MODERATE TO SEVERE DRY EYE SYNDROME
Participants were asked to rank, in order of overall importance, the goals of treatment for moderate to severe DED. On a scale of 1 (most important) to 6 (least important), respondents could rank among the following options: prolonging tear film breakup time, stimulating tear production, lubricating and hydrating the ocular surface, inhibiting inflammatory factors, helping patients tolerate contact lenses, and maintaining and protecting the ocular surface. As summarized in Figure 2, survey participants indicated that the most important goal of DED treatment is maintenance and protection of the ocular surface (mean score, 1.0), followed closely by lubrication and hydration of the ocular surface (mean score, 1.4).
FIGURE 2.
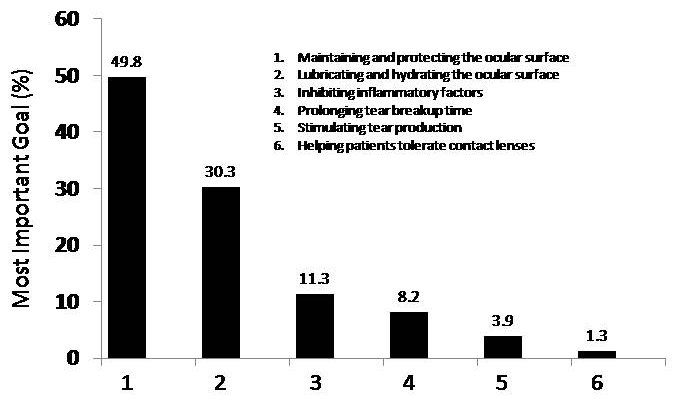
Most important goal for the treatment of moderate to severe dry eye syndrome expressed as mean percentage of total responses.
Survey respondents were asked to rank determinants of successful treatment of moderate to severe DED on a scale of 1 (most important) to 7 (least important). Criteria for measuring successful treatment included lengthening of tear film breakup time, decrease in rose bengal, fluorescein, or lissamine green staining, increase of Schirmer test score, improved vision, relief of symptoms/patient satisfaction, increase in tear film meniscus, and prevention of damage to the cornea. As summarized in Figure 3, participants indicated that relief of symptoms/patient satisfaction (mean score, 1.0) was the most important determinant of successful treatment for moderate to severe DED, followed by prevention of damage to the cornea (mean score, 2.5).
FIGURE 3.
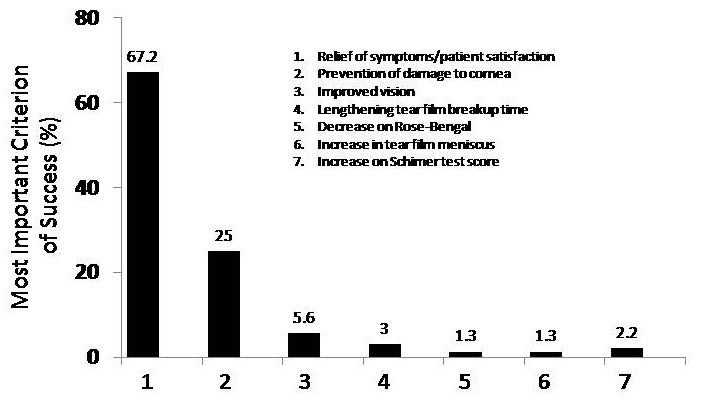
Most important criteria of successful treatment of moderate to severe dry eye syndrome expressed as mean percentage of total responses
The survey also asked participants to estimate how many different treatment approaches they prescribe or recommend for mild, moderate, and severe DED over the course of 1 year. Respondents prescribe or recommend an average of 1.9 treatment approaches for mild DED, 3.2 approaches for moderate DED, and 4.9 approaches for severe DED. 23.4% of the participants were using four or more approaches to treat moderate dry eye, while 72.1% were using four or more approaches to treat severe dry eye. (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
NUMBER OF ANNUAL DRY EYE SYNDROME PRESCRIPTIONS OR TREATMENT RECOMMENDATIONS PER PATIENT*
| DISEASE SEVERITY | NO. OF TREATMENT APPROACHES | TOTAL MEAN | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4–5 | 6–7 | 8–10 | 11+ | ||
| Mild | 0.4% | 36.1% | 47.4% | 12.2% | 3.0% | 0.4% | 0% | 0.4% | 1.9 |
| Moderate | 0.4% | 0.9% | 27.7% | 47.6% | 18.2% | 4.8% | 0.4% | 0% | 3.2 |
| Severe | 0.4% | 0.9% | 3.1% | 23.6% | 47.6% | 14.8% | 6.6% | 3.1% | 4.9 |
Based on survey question: On average, over the course of a year of treating a dry eye patient, approximately how many different treatment approaches do you prescribe, recommend, or suggest?
Participants were also asked to select which qualities of treatment options for DED they take into consideration when developing a treatment plan for a patient with moderate to severe DED. Respondents could select from a list including preservative-free, dosing frequency, length of time preserving the tear film, length of time to effectiveness, patient acceptance, ability to use with contact lenses, ability to provide continuous relief, ability for concomitant use with other medications, and ability to use long-term. The treatment characteristics participants most frequently selected as key considerations (summarized in Table 2) were the ability to provide continuous relief (84.2% of participants selected this answer) and patient acceptance (82.5% of participants chose this response).
TABLE 2.
KEY CHARACTERISTICS OF THERAPIES FOR MODERATE TO SEVERE DRY EYE SYNDROME*
| QUALITY OF TREATMENT OPTION | N | % RESPONDENTS SELECTING ANSWER |
|---|---|---|
| Ability to provide continuous relief | 197 | 84.2 |
| Patient acceptance | 193 | 82.5 |
| Ability to use long-term | 173 | 73.9 |
| Dosing frequency | 155 | 66.2 |
| Length of time preserving the tear film | 155 | 66.2 |
| Length of time to effectiveness | 148 | 63.2 |
| Preservative-free | 126 | 53.8 |
| Ability to use with contact lenses | 119 | 50.9 |
| Ability for concomitant use with other medications | 102 | 43.6 |
| Other (please specify) | 9 | 3.8 |
Based on the survey question: When selecting products for moderate to severe dry eye patients, which of the following are key considerations? (Multiple responses allowed.)
AREAS OF CONCERN WHEN TREATING MODERATE TO SEVERE DRY EYE SYNDROME
The survey asked respondents to indicate how effective they feel current therapies for mild, moderate, and severe DED are, ranging from extremely effective to not effective at all. The majority of participants (79.9%; n = 187) indicated that current treatments for mild DED are extremely or very effective, whereas 32.5% (n = 76) ranked therapies for moderate DED in this category. Twelve (5.1%) of the respondents indicated that current treatments for severe DED are extremely or very effective, and 38.2% (n = 89) felt that therapies for severe DED are not very or not at all effective.
Participants were also asked to provide their opinion of a set of presented statements, including whether more treatment options are needed for moderate to severe DED, treatment of DED can help establish a practice, DED is difficult to diagnose, the signs and symptoms of moderate to severe DED can be improved but seldom eliminated, there is a treatment gap between artificial tears and more aggressive treatments for moderate to severe DED, and multiple therapeutic agents are usually needed to manage moderate to severe DED. As summarized in Table 3, the majority of respondents agreed that more treatment options are needed for moderate to severe DED (94.4%; n = 219). Corneal specialists were more likely to strongly agree (63%) than general ophthalmologists (54%). Participants also agreed that multiple therapeutic agents are usually necessary to manage moderate to severe disease (92.3%; n = 215), that a gap exists between treatment with artificial tears and more aggressive therapy for moderate to severe DED (82.7%; n = 191), and that while signs and symptoms may improve, they are seldom eliminated (81.1%; n = 189). The majority of participants (80.6%; n = 187) disagreed with the statement that DED is difficult to diagnose.
TABLE 3.
RESPONDENT LEVEL OF AGREEMENT TO A SET OF STATEMENTS ABOUT DRY EYE SYNDROME
| STATEMENT | STRONGLY AGREE (%) | SOMEWHAT AGREE (%) | SOMEWHAT DISAGREE (%) | STRONGLY DISAGREE (%) | TOTAL (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| More treatment options are needed for moderate/severe dry eye | 55.6 | 38.8 | 4.7 | 0.9 | 232 |
| Multiple therapeutic agents are usually needed to manage moderate/severe dry eye | 41.6 | 50.6 | 6.4 | 1.3 | 233 |
| Treating dry eye can help build my practice | 34.8 | 52.4 | 9.9 | 3.0 | 233 |
| There is a treatment gap between artificial tears and more aggressive moderate/severe dry eye treatments | 20.3 | 62.3 | 16.0 | 1.3 | 231 |
| Signs and symptoms of moderate/severe dry eye can be improved but seldom eliminated | 28.8 | 52.4 | 17.2 | 1.7 | 233 |
| Dry eye is difficult to diagnose | 1.7 | 17.7 | 53.4 | 27.2 | 232 |
DISCUSSION
The results of this survey provide insight into the current perceptions of moderate to severe DED and its treatment held by comprehensive ophthalmologists and corneal specialists throughout the United States. Only 10 of the 245 participants in this survey (4.1%) indicated that they see fewer than 4 DED patients per month, emphasizing the common clinical presentation of the disease. Consistent with the accepted etiology of DED, respondents confirmed that the disease is indeed multifactorial in nature. DED is a multifactorial disorder of the tears and ocular surface that results in symptoms of discomfort, visual disturbance, and tear film instability and poses a risk of potential damage to the ocular surface. It is accompanied by increased osmolarity of the tear film and inflammation of the ocular surface.1 While environmental conditions of low humidity and postmenopausal hormonal changes were indicated as leading primary causes of DED, systemic medications, use of contact lenses, eye/eyelid injury, Sjögren syndrome, and LASIK or other ocular surgery were identified as major primary causes with approximately equal frequency.
Respondents indicated that successful management of the disease is often measured by patient-reported improvement in symptoms and overall satisfaction. It is of particular interest that although the majority of participants in this survey identify inflammation as an underlying cause of DED, they identify protection of the ocular surface and lubrication of the eye as the most important goals of treatment. Therefore, treatment choices should consider the negative impact of preservatives such as benzalkonium chloride, found in some dry eye solutions. Their effects on the cornea and conjunctival epithelium led members of the Management and Therapy Subcommittee of the Dry Eye Workshop (DEWS) 4 to recommend preservative-free ocular lubricants.
As expected, respondents indicated that they prescribe or recommend more treatment options for increasingly advanced DED. The majority of participants stated that current treatment options for patients with severe DED are not effective and that a gap exists between currently available artificial tears and effective therapy. Participants identified a clear need for additional options that provide continuous relief of DED symptoms and that are acceptable to patients. A preservative-free therapeutic option that provided continuous, long-term relief of DED symptoms would be highly desirable.
Data obtained from surveys of this type have inherent biases that should be acknowledged. Respondents were limited to those ophthalmologists who could be reached online, and the percentage of respondents was, as is typical of such surveys, relatively small (3.1%) and may not be entirely representative of the overall population. Despite these limitations, the demographics of the respondent group indicated that respondents were well distributed geographically and were representative of the full range of ophthalmologic practice.
While the results of this survey provide insight into ophthalmologists’ current perceptions and treatment of patients with moderate to severe DED, they do not address patients’ perceptions of the disease. A future survey to compare patients’ responses may provide additional insight due to the general lack of correlation between the signs and symptoms of DED.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Funding/Support: Supported by Aton Pharma Inc, Lawrenceville, New Jersey.
Financial Disclosures: Dr Asbell and Dr Spiegel are consultants for Aton Pharma. Dr Asbell also receives grant support from Aton Pharma.
Author Contributions: Design of the study (P.A., S.S.); Conduct of the study (P.A.); Management, analysis, and interpretation of data (P.A., S.S.); Preparation, review, or approval of manuscript (P.A., S.S.).
Conformity With Author Information: An institutional review board waiver was provided to conduct this survey.
Other Acknowledgments: The authors would like to thank Ed Stevens, MEd, for his assistance with developing the survey questionnaire and Norman Nagl, PhD, and Donald Nelinson, PhD, for editorial assistance in preparation of this manuscript.
REFERENCES
- 1.The definition and classification of dry eye disease: report of the Definition and Classification Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye Workshop (2007) Ocul Surf. 2007;5:75–92. doi: 10.1016/s1542-0124(12)70081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lemp MA. Advances in understanding and managing dry eye disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008;146:350–356. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2008.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.The epidemiology of dry eye disease: report of the Epidemiology Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye Workshop (2007) Ocul Surf. 2007;5:93–107. doi: 10.1016/s1542-0124(12)70082-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Management and therapy of dry eye disease: report of the Management and Therapy Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye Workshop (2007) Ocular Surf. 2007;5:163–178. doi: 10.1016/s1542-0124(12)70085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]