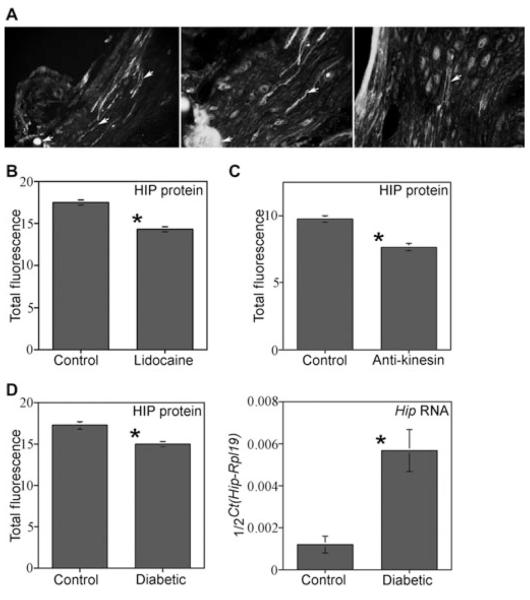
Figure 6.
Hedgehog-interacting protein (HIP) localization and quantification in the cavernous nerve (CN) tie, lidocaine, anti-kinesin-treated Sprague-Dawley rats, and in diabetic rats. (A) A tie was placed on the CNs in order to determine if HIP protein was under going anterograde transport to the penis via the CN. HIP protein built up on the ganglia side of the tie after 2 days (left and middle, ×100, and right, ×250) showing that HIP protein was transported by the CN. HIP protein was observed originating in neurons of the pelvic ganglia (Right, ×160). (B) HIP protein was significantly decreased 1.2-fold in corpora cavernosa of rats in which their CN’s were treated with lidocaine. (C) HIP was significantly decreased 1.3-fold in corpora cavernosa of rats in which their CN’s were treated with anti-kinesin. (D) HIP protein was significantly decreased 1.2-fold in diabetic penises and Hip RNA expression was increased 3.1-fold in diabetic penises.