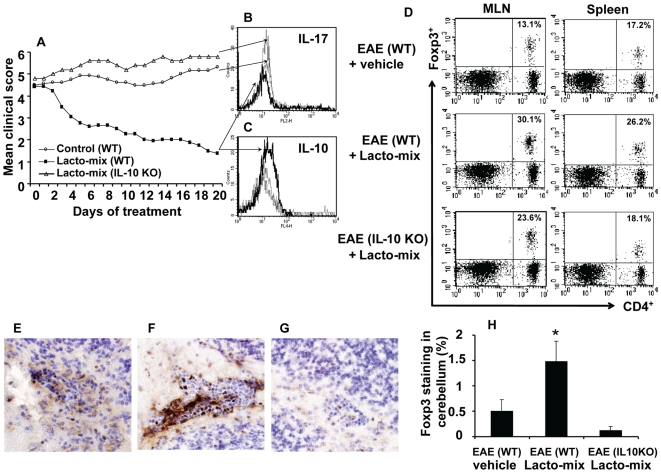
Figure 4. Probiotic treatment suppresses IL-17 expression and favors Treg emergence in an IL-10-dependent manner.
C57BL/6 wild type (WT) or IL-10-KO mice were immunized and observed for clinical signs of EAE. Fourteen days after the onset of EAE, animals were orally treated with a mixture of lactobacilli (Lacto-mix) or saline as control. (A) The mean clinical score for each group of mice is shown. Data represent pooled values from two independent experiments. Histograms show the expression of (B) IL-17 and (C) IL-10 by CD4+ T cells freshly isolated from the brain of Lacto-mix-treated WT (thick line), IL-10 KO (dashed line), or saline-treated control mice (thin line), after 20 days of therapeutic treatment. (D) MLNs and spleens isolated from these animals were analysed by flow cytometry for expression of CD4, CD25 and Foxp3. Presented FACS plots show the percentage of CD4+Foxp3+ cells of the total CD4+ T cells (numbers in quadrants) in control EAE (top panel), Lacto-mix-treated WT (middle panel), or IL-10 KO (bottom panel) mice. The presence of infiltrating Foxp3+ cells into the cerebellum parenchyma and perivascular cuffs was assessed by immunohistochemical staining of sections from (E) control EAE, (F) Lacto-mix-treated WT, (G) Lacto-mix-treated IL-10 KO. (H) In the histogram, each bar represents the mean percentage of Foxp3 stained area (± SEM) from 3 mice per treatment group. Data are representative of two experiments. * represents a p-value ≤0,05.