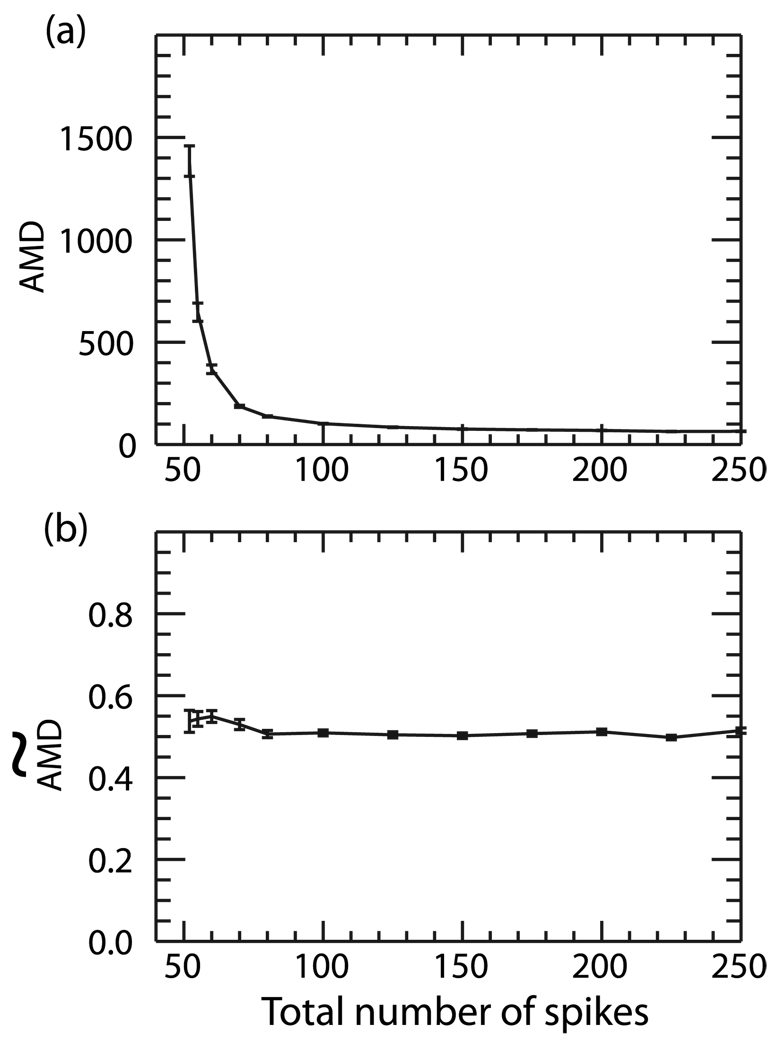
FIG. 2.
(a) AMD and (b) 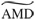 calculated between two random Poisson trains as a function of the total number of spikes in the trains. One spike train contained a constant number of 50 spikes while the spiking frequency in the other was varied between 2 and 200 spikes. While the AMD scales with the number of spikes in the trains, the
calculated between two random Poisson trains as a function of the total number of spikes in the trains. One spike train contained a constant number of 50 spikes while the spiking frequency in the other was varied between 2 and 200 spikes. While the AMD scales with the number of spikes in the trains, the 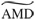 remains constant as the number of spikes is varied.
remains constant as the number of spikes is varied.